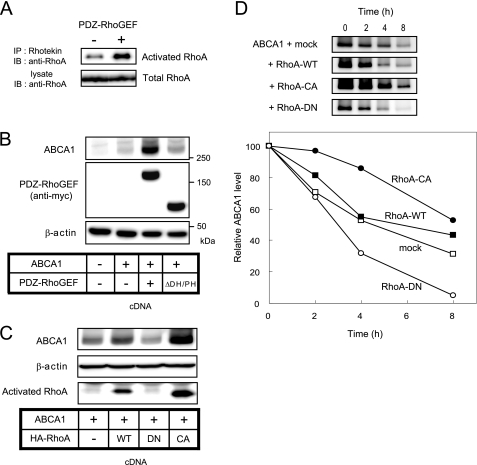
FIGURE 3.
RhoA activation by PDZ-RhoGEF increase the ABCA1 protein levels by blocking its degradation. A, the expression of PDZ-RhoGEF increases the amount of activated RhoA. The transfected cells were lysed, and activated RhoA was precipitated with Rhotekin-RBD beads. Precipitates or lysates were immunoblotted with anti-RhoA to detect activated and total RhoA, respectively. B, the ability of PDZ-RhoGEF to enhance ABCA1 expression was attenuated in cells expressing PDZ-RhoGEF ΔDH/PH mutant. 293 cells were transfected with vector alone, ABCA1 cDNA alone, or ABCA1 cDNA together with PDZ-RhoGEF cDNA or PDZ-RhoGEF cDNA mutant lacking the DH and PH domain (ΔDH/PH). C, RhoA directly regulates ABCA1 protein expression. The cells were co-transfected with ABCA1 and either HA-tagged wild-type RhoA (WT), a dominant negative form of RhoA (DN), a constitutively active form of RhoA (CA), or with empty vector. The results in A–C are representative of two or more experiments. D, activated RhoA blocks, and inactivated RhoA enhances the ABCA1 degradation. The cells were co-transfected with ABCA1 and wild-type RhoA, RhoA-CA, RhoA-DN, or empty vector. Cycloheximide was added to block protein synthesis 24 h after transfection. The cells were lysed after the indicated times, and the lysates were immunoblotted with anti-ABCA1 antibody. Shown are representative images, and graphed are the average values expressed as percentage of increase of the amount of ABCA1 quantified by LAS-3000 imager in two (mock and RhoA-DN) or three (wild type RhoA and RhoA-CA) separate experiments. IB, immunoblotting; IP, immunoprecipitation.