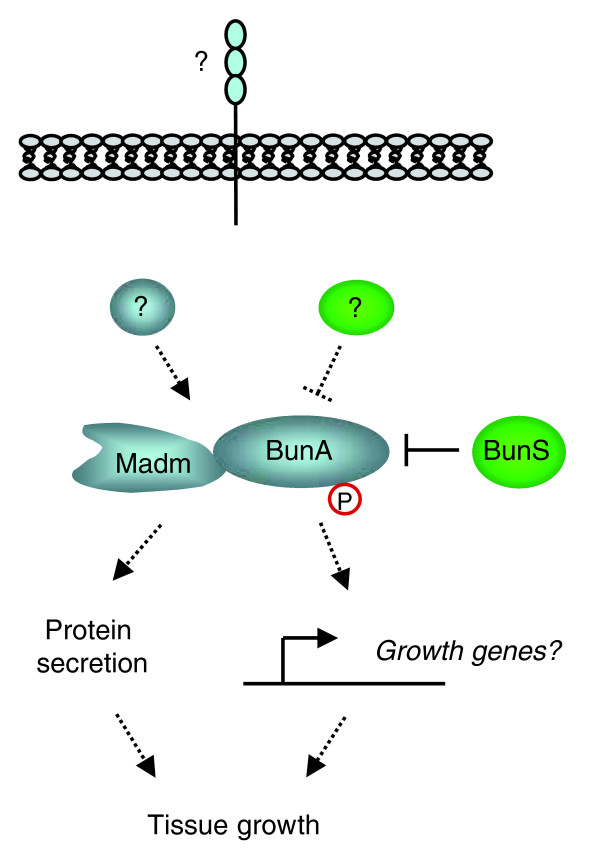
Figure 1.
The Bun-Madm growth-regulatory complex. Long isoforms of Bun (such as BunA) promote tissue growth in partnership with Madm. Short Bun isoforms (BunB-E, collectively denoted BunS) can antagonize BunA, thus inhibiting its function. The existence of other unknown proteins (question marks), such as a transmembrane receptor protein, that function either upstream or downstream of the BunA-Madm complex is currently unclear (dashed lines). The mechanism by which the BunA-Madm complex is regulated probably involves BunA phosphorylation (P). BunA and Madm are likely to promote growth by controlling transcription and/or protein secretion.