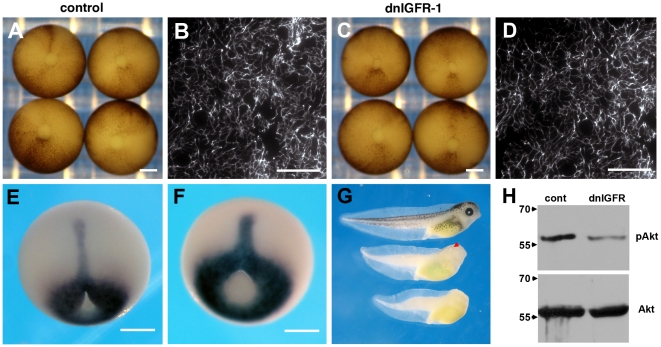
Figure 6. Inhibition of FN matrix assembly is not due to IGF signaling.
(A, B) Control embryos close the blastopore by stage 12 and elaborate a dense FN matrix. (C, D) Embryos expressing a dominant negative IGFR-1 construct (dnIGFR-1) appear similar to control embryos and elaborate a dense FN matrix. (E) Xbra expression in control embryos. (F) Xbra patterning is not altered by blocking IGF signaling. There is a minor effect on axial extension that is clearly revealed in tadpoles (G) Control tadpoles (top) are longer than tadpoles resulting from embryos expressing dnIGFR-1 (middle). The dnIGFR-1 construct results in anterior defects including reduced or absent eyes (arrowhead). Tadpoles obtained from embryos that express kermit2mut show severe anterior truncations and mesodermal defects (bottom). (H) Western blots demonstrating inhibition of IGF signaling by the dnIGFR-1 construct. The phosphorylation of Akt (pAkt) seen in controls (cont) is not maintained in animal caps that express the dominant negative IGFR-1 construct (dnIGFR). Bottom panel shows total Akt expression in the same lysate. Molecular mass is indicated to the left of the panel.