Table 1.
List of selected existing optimality hypotheses. V is the mean flow velocity, S is the channel slope, ρ is the density of water, g is the gravitational acceleration constant, Q is the flow discharge, L is the reach length, ρs is the density of sediment, Qs is the sediment transport rate, W is the channel width, H is the hydraulic depth, and η is a constant. Qj and Lj are the discharge and the length of link j (channel between two confluences), respectively. In application of these hypotheses, Q and Qs are treated as given constants, and channel or network geometry is adjusted to obtain the optimal combination of variables such as V, S, H, W and L to satisfy a given objective function.
| hypotheses | mathematical form | references |
|---|---|---|
| MUSP | min VS | Brebner & Wilson (1967); Yang (1973, 1976) |
| MSP =MSTC | min ρgQS | Chang & Hill (1977); Chang (1979a); White et al. (1982) |
| MEDR | min (ρgQ + ρsgQs)LS | Yang et al. (1981) |
| MFF | max W2H3S/Q2 | Davies & Sutherland (1980, 1983) |
| minimum Froude number | min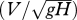
|
Jia (1990) |
| minimum total energy expenditure | min 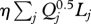
|
Rodríguez-Iturbe et al. (1992) |
