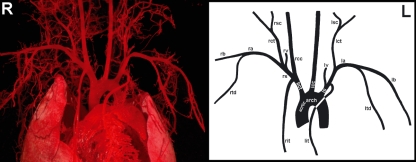
Fig. 2.
Ventral view of a cast (left side of the figure) and schematically drawn (right side of the figure) murine aortic arch with its originating arteries (R and L = right and left side of the thorax, respectively). bct, brachiocephalic trunk; rit, right internal thoracic artery; rs, right subclavian artery; rcc, right common carotid artery; rv, right vertebral artery; rct, right cervical trunk; rsc, right superficial cervical artery; ra, right axillary artery; rb, right brachial artery; rtd, right thoracodorsal artery; lcc, left common carotid artery; ls, left subclavian artery; lit, left internal thoracic artery; lv, left vertebral artery; lct, left cervical trunk; lsc, left superficial cervical artery; la, left axillary artery; lb, left brachial artery; ltd, left thoracodorsal artery. Notice that the right internal thoracic artery in this specimen branches off from the long brachiocephalic trunk.