Fig. 4.
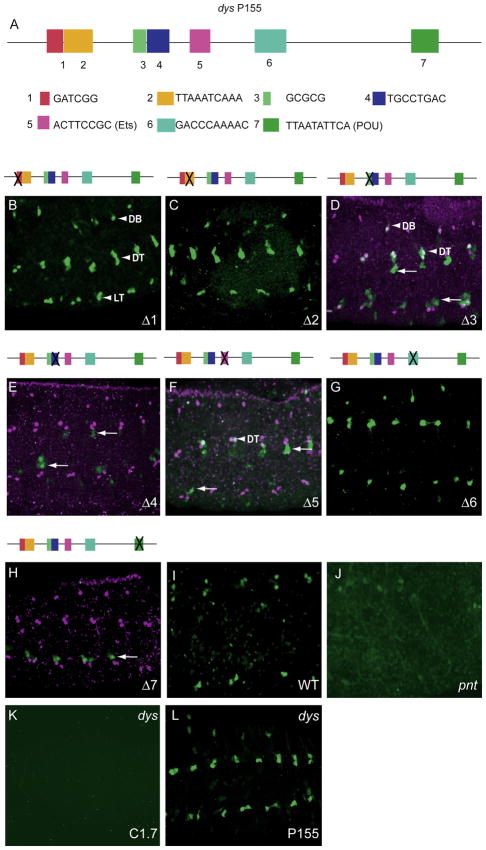
Mutational analysis of dys P155 fragment identified several sites required for fusion cell expression. (A) Schematic of P155 showing the conserved sequences (1–7) that were deleted and assayed for fusion cell expression. (B–H) The Δ1, Δ2, and Δ6 deletions had no effect on fusion cell expression, whereas the Δ4 and Δ7 deletions abolished expression, and the Δ3 and Δ5 deletions resulted in GFP expression in only a few DB and DT cells (arrowheads). Arrows indicate GFP-expressing non-fusion cells. (I,J) Expression of dys (anti-Dys; magenta) in fusion cells (I; wild-type control) was reduced in (J) pntΔ88 mutant embryos. The gain was increased in (J) to show that GFP was weakly present (and not absent) in pntΔ88 DT. (K,L) GFP expression of dys C1.7 was abolished in a dys1 mutant, whereas expression of dys P155 was unaffected.