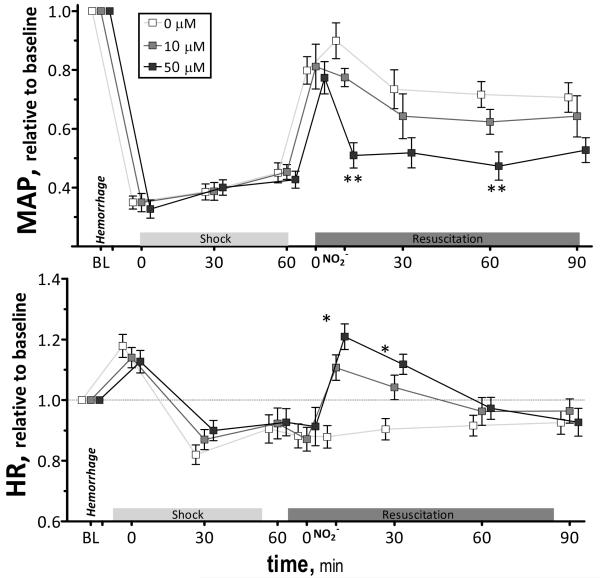
Figure 1.
Relative changes in mean arterial pressure (MAP) and heart rate (HR) during hemorrhagic shock resuscitation for all groups. Mean arterial pressure (mmHg, mean ± SD) in each animal group were as follows: Baseline: 0μM (106 ± 9, n = 6); 10μM (A: 109 ± 8, n = 6); 50μM (A: 107 ± 9, n = 6). Heart rate (bpm, mean ± SD) in each animal group were as follows: Baseline: 0μM (436 ± 26, n = 6); 10μM (A: 429 ± 25, n = 6); 50μM (A: 447 ± 29, n = 6). n = number of vessels studied. Broken line represents baseline level. **, P<0.05, 50μM compared to 0μM and 10μM; *, P<0.05, 50μM compared to 0μM.