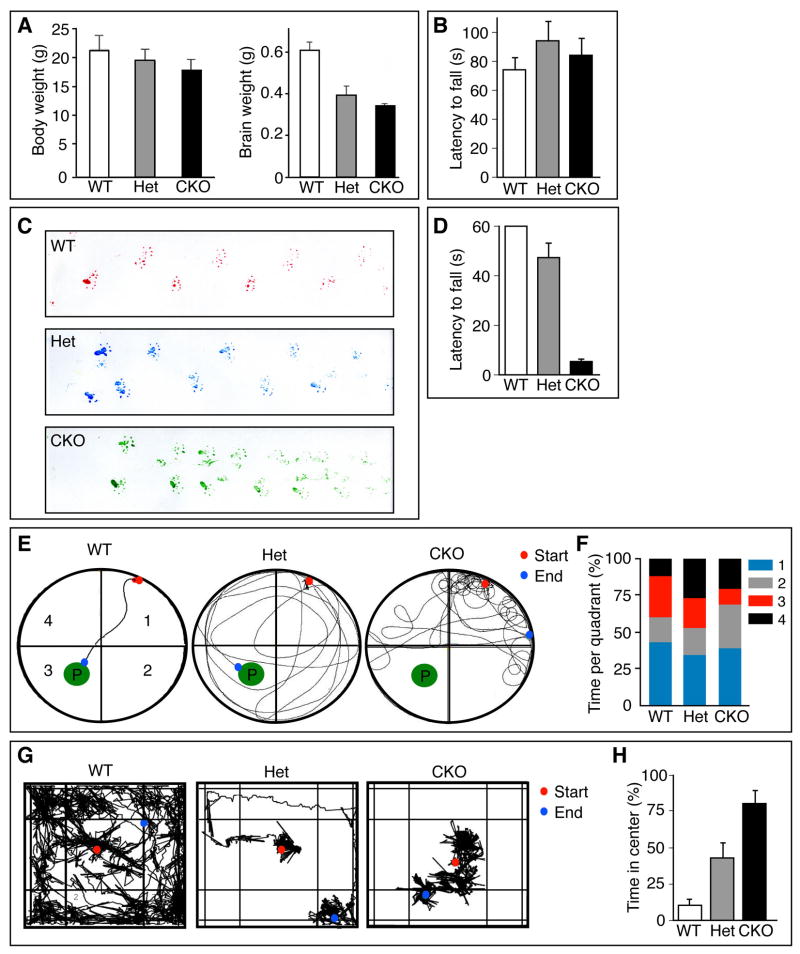
Figure 2. Pals1 loss reveals dorsal cortex-dependent and -independent behaviors.
(A) Body and brain weight of littermates at 4 weeks of age. The brain mass of Pals1 CKO and Pals1 Het mice are smaller than WT (t-test, p<0.001; n=3–5). (B) Mice tested on the accelerating rotarod showed no significant differences between Pals1 CKO, Pals1 Het, or control mice. (C) Similar footprint patterns of wild type (top), Pals1 Het (middle), and Pals1 CKO (bottom) mice. (D) Pals1 CKO mice had reduced latency to fall in the wire hang test versus controls and Pals1 Het mice (t-test: p<0.0005 and p<0.05, respectively, n=10). (E) Representative traces of swimming patterns of WT (left), Pals1 Het (middle), and Pals1 CKO (right) mice in a Morris water maze where mice swam towards a visible platform (P) located in quadrant 3. (F) Quantification of time spent per quadrant during swimming trial in (E). Pals1 CKO mice spent the least time in the quadrant with the platform versus wild type and Pals1 Het mice (t-test: p<0.005; n=10). (G) Representative traces of exploratory behavior of WT (left), Pals1 Het (middle), and Pals1 CKO (right) mice during a 10 minute open field trial. (H) Quantification of time spent in center quadrant during open field test (G). Pals1 Het and Pals1 CKO mice spent less time exploring the open field versus WT controls (t-test: p<0.05 and p<0.0005, respectively; n=10).