Figure 1.
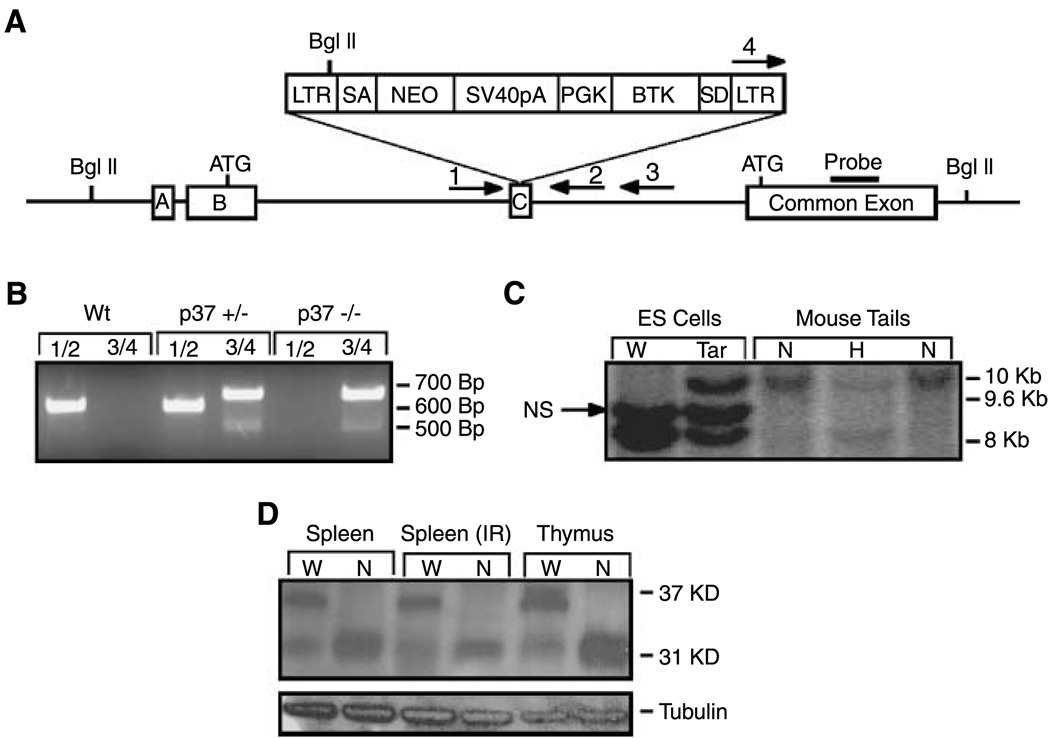
Generation of p37Ing1-deficient mice. A, schematic of the gene-trapped locus showing the gene trap inserted into exon C. The trap interrupts the Ing1b message isoform and corresponding p37 protein but encodes the shorter Ing1c isoform and p31 protein. B, PCR genotyping of the embryonic stem cells and mouse tail biopsies showing the presence of the gene trap. A 650-bp fragment is generated from Wt Ing1 using primers 1 and 2 and a 700-bp fragment is generated from the targeted Ing1 allele using primers 3 and 4. C, a Southern blot strategy using a BglII digest and a probe to the common exon was used to confirm germ-line transmission of the gene trap. The Wt fragment is ~8 kb and the mutant fragment is ~10 kb in length. A nonspecific (NS) band corresponding to an Ing1 pseudogene present in 129 strain mouse DNA is also observed. D, to confirm that the longer p37Ing1 form was specifically deleted, a Western blot was done with an Ing1 antibody that recognizes sequences encoded in the common exon. The presence of the shorter form (p31) and the absence of the longer form (p37) were observed. Tubulin was used as a loading control.