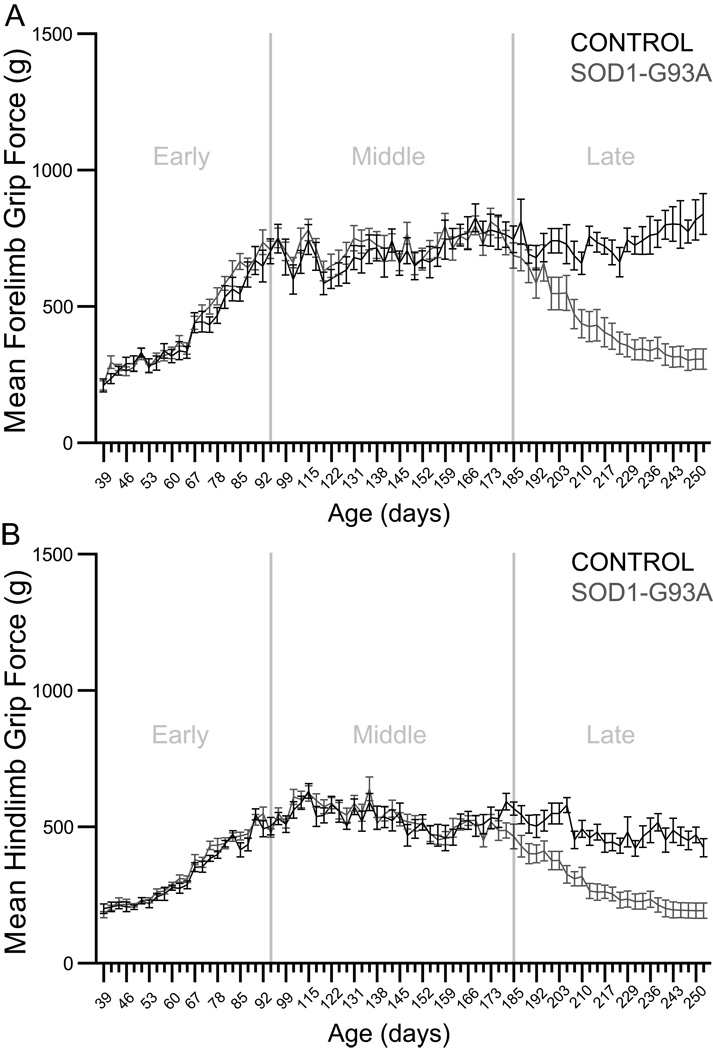
Figure 3.
Panel A: Forelimb grip strength. Graph depicts the mean forelimb grip force in grams (± S.E.M.) during the early, middle, and late phases of the disease in control and SOD1-G93A rats. In the early and middle phases, analyses yielded significant effects of time (p<0.0001 in both cases). In the late phase, analysis yielded significant effects of genotype (p<0.0001) and time (p<0.0001), as well as a significant genotype × time interaction (p<0.0001). Panel B: Hindlimb grip strength. Graph depicts the mean hindlimb grip force in grams (± S.E.M.) during the early, middle, and late phases of the disease in control and SOD1-G93A rats. In the early and middle phases, analyses yielded significant effects of time (p<0.0001 in both cases) and significant genotype × time interactions (early phase p=0.0470; middle phase p=0.0154). In the late phase, analysis yielded significant effects of genotype (p<0.0001) and time (p<0.0001), as well as a significant genotype × time interaction (p<0.0001).