Figure 4.
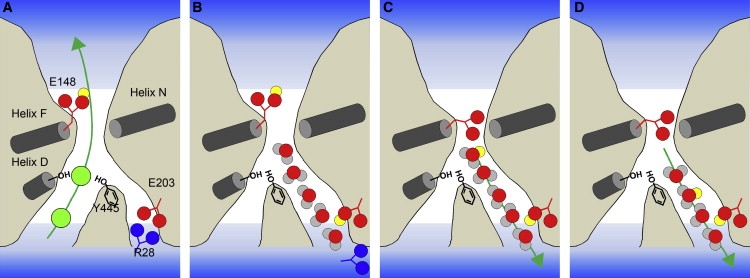
Schematic representation of the coupled movement of chloride ions and protons. The D-, F-, and N-helices are represented by gray cylinders. (A) Chloride ions are represented as green spheres, and protons are represented as yellow spheres. Protonation of E148 causes the primary pore to be opened, which results in chloride ion conduction. (B) After the chloride ions pass through the primary pore, the interaction between E203 and the R28 is broken due to the protonation of E203, resulting in the formation of a water network in the secondary pore. (C) The proton belonging to E148 is transferred to a water molecule inside the secondary pore, and subsequently the primary pore is closed by the deprotonation of E148. (D) The proton passes through the secondary pore via the water network.
