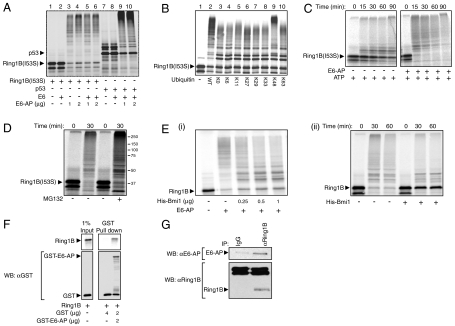
Fig. 2.
Ring1B is ubiquitinated and targeted for degradation by E6-AP in vitro. (A) In vitro translated and 35S-labeled Ring1BI53S and p53 were ubiquitinated in a cell free reconstituted system in the presence or absence of recombinant E6 and His-E6-AP as indicated. (B) 35S-labeled Ring1BI53S was conjugated in a cell free reconstituted system in the presence of ubiquitin species that contain the indicated lysine residues. (C and D) 35S-labeled Ring1BI53S was subjected to in vitro degradation in the presence of ATP and an ATP-regenerating system, E6-AP, and MG132 (20 μM) as indicated. (E) Ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of Ring1B by E6-AP is inhibited by the addition of Bmi1. 35S-labeled Ring1B was subjected to in vitro ubiquitination (i) and degradation (ii) in the presence of His-E6-AP and His-Bmi1 as indicated. Conjugation and degradation assays were carried out as described under Materials and Methods. The SDS-PAGE resolved proteins were visualized via PhosphorImaging. (F) 35S-labeled WT Ring1B was pulled down by GST or GST-E6-AP using glutathione beads. The SDS-PAGE-resolved proteins were visualized using PhosphorImaging (Ring1B) or following Western blotting (GST). (G) Endogenous Ring1B was immunoprecipitated from U2OS cell extract using a specific antibody. The precipitates were resolved via SDS-PAGE and analyzed for the presence of E6-AP and Ring1B using specific antibodies.