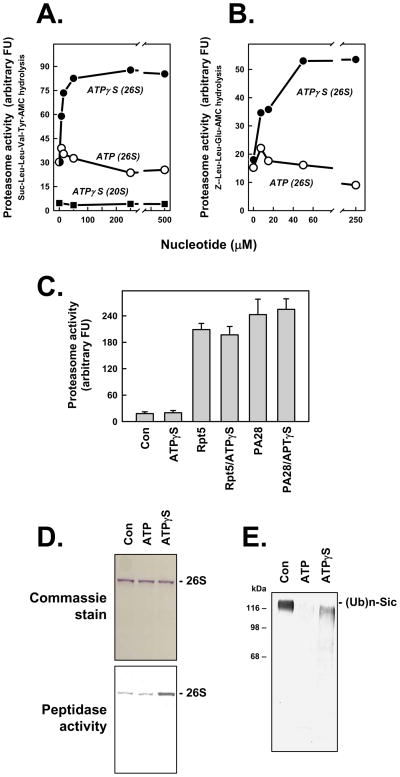
Figure 1. ATPγS stimulates peptidase activity of the 26S proteasome.
Panels A and B. 26S proteasome (0.7 nM) or 20S proteasome (2 nM) was assayed for peptidase activity using indicated substrates. Assays for 26S proteasome contained 5 μM ATP and indicated additional concentrations of either ATP or ATPγS. Assays for 20S proteasome contained indicated concentations of ATPγS. Data points represent mean values of triplicate assays. Similar effects were obtained in four independent experiments. Panel C. 20S proteasome (2 nM) was assayed for peptidase activity using Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-TryAMC substrate and indicated effectors: ATPγS (500 μM); Rpt5 (10 residue peptide of the C-terminus of Rpt5 PA700 subunit, 400 μM); Rpt5 (400 μM) and ATPγS (500 μM); PA28 (200 nM); PA28 (200 nM) and ATPγS (500 μM). Data represent mean values of quadruplicate assays (+/− SD). Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. Panel D. 26S proteasome was preincubated with 10 μM (Con), 400 μM ATP (ATP) or 10 μM ATP and 400 μM ATPγS (ATPγS) and then subjected to native PAGE. One half of the get was stained with Commassie blue (upper panel) and the one half of the gel was incubated with Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Tyr-AMC for 15 mins at 37°C and exposed to UV light to reveal AMC product (lower panel); the lower image has been converted to a positive exposure. Panel E. Polyubiquitylated-Sic was incubated in the absence (Con) or presence of 26S proteasome with 200 μM of either ATP or ATPγS, as described in Experimental Procedures. Samples were subjected to western blotting using anti-His antibody.