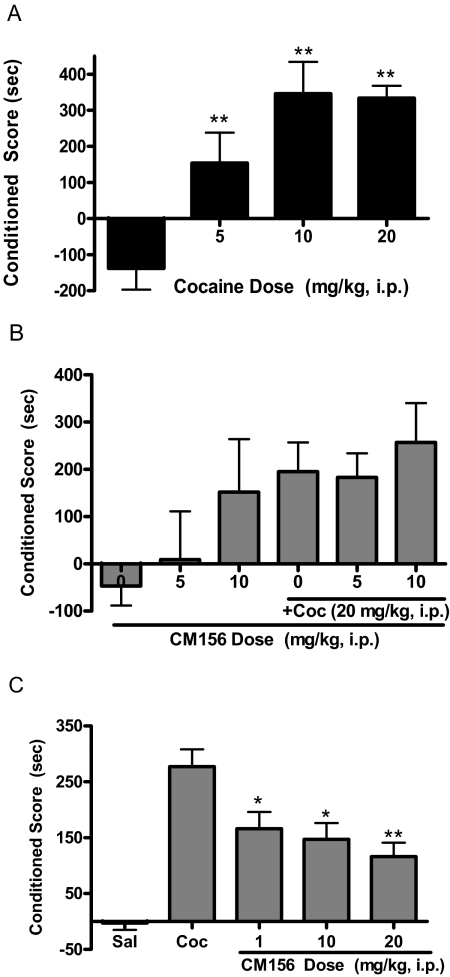
Fig. 6.
Place conditioning. A, administration of cocaine (0–20 mg/kg i.p.) produced a dose-dependent increase in place conditioning in mice. Mice were injected four times with a dose of cocaine (0–20 mg/kg i.p.) and confined to half of a place conditioning chamber; they received saline on an alternating schedule and were confined to the other side of the chamber. B, CM156 had no significant effect on the development of cocaine-induced place conditioning. Mice were injected with saline or CM156 (5 and 10 mg/kg i.p.) 15 min before saline or cocaine (+Coc; 20 mg/kg i.p.) during conditioning sessions; they remained drug-free on the postconditioning test day. None of the changes were statistically significant. C, CM156 significantly attenuated the expression of cocaine-induced place conditioning. Mice were injected with saline (Sal) or cocaine (Coc; 20 mg/kg i.p.) during the conditioning sessions; they received CM156 (1–20 mg/kg i.p.) 15 min before the postconditioning test session. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; post hoc tests.