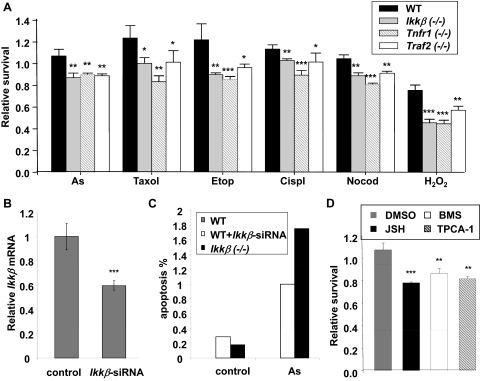
Fig. 2.
IKKβ and NF-κB inactivation reduces cell survival in response to oxidative damage. A, wild-type and gene-knockout fibroblasts were treated for 24 h with various oxidative agents, including 10 μM sodium arsenite (As), 50 μM hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), 50 μM cisplatin (Cispl), 50 μM etoposide (Etop), 5 μM paclitaxel (Taxol), and 5 μM nocodazole (Nocod). Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. B, wild-type fibroblasts were transfected with either scrambled or Ikkβ-siRNA (100 nM). The relative Ikkβ expression was determined by real-time RT-PCR. The Ikkβ levels in scrambled RNA transfected cells are designated as 1. C, the wild-type cells with or without Ikkβ-siRNA transfection and Ikkβ(−/−) cells were treated with 50 μM arsenic for 2 h. Apoptosis was measured by TUNEL assay. The values represent the average of at least 400 cells counted. D, wild-type fibroblasts treated for 2 h with 0.1% DMSO, 10 μM JSH23, 1 μM BMS-345541, and 0.5 μM TPCA-1, followed by treatment with 10 μM sodium arsenite for 24 h. Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. All results are presented as the mean values ± S.E. from at least three independent experiments. Statistical analyses were done compared with the mean values in control wild-type cells and **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 were considered significant.