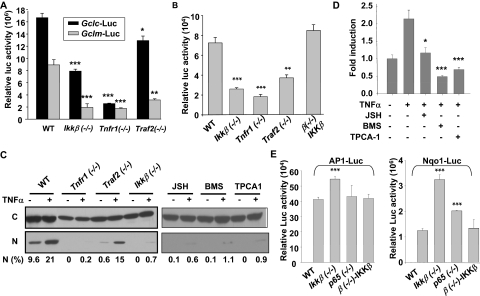
Fig. 4.
Inactivation of the IKKβ pathway affects transcription factor activities. A, wild-type, Ikkβ(−/−), Tnfr1(−/−), and Traf2(−/−) cells were transfected with β-gal expression plasmids together with Gclc-Luc and Gclm-Luc. The relative luciferase activities were normalized to β-galactosidase activities measured 24 h after transfection. Wild-type, various knockout cells, and Ikkβ(−/−) cells infected with Ad IKKβ [β(−/−)-IKKβ] were transiently transfected with β-gal expression plasmids, together with and AP-1-luc (B) and Nqo1-luc (E). D, wild-type cells were transfected with NF-κB-luc and β-gal plasmids for 24 h, followed by inhibitor and TNFα treatment for 16 h. The relative luciferase activities were normalized to β-galactosidase activities measured 24 h after transfection. All results are presented as the mean values ± S.E. from at least three independent experiments. Statistical analyses were done compared with the mean values in control wild-type cells and **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 were considered significant. C, cells were either untreated or treated with TNFα (10 ng/ml) for 0.5 h. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts from 500,000 cells were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-p65 and the relative levels of nuclear p65 [N (%)] were calculated after densitometric quantification of chemiluminescence.