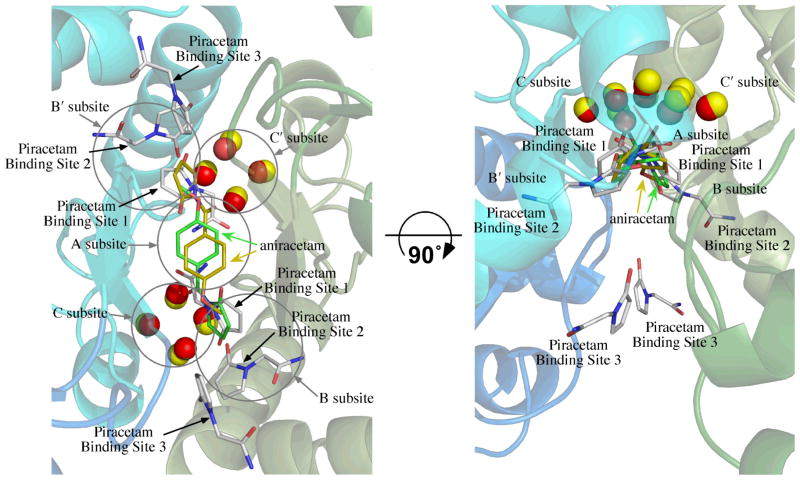
Figure 2.
Overlay of the position of aniracetam bound to GluA2o (fluorowillardiine in the agonist binding site, 2AL5)30 on the structure of piracetam bound to GluA2i (glutamate in the binding site). One molecule of aniracetam is bound to a given dimer interface, but since the interface is symmetrical, two orientations are observed. One is shown with carbons colored yellow and the other with carbons colored green. The water molecules from the aniracetam structure are shown as yellow spheres. The six molecules of piracetam are shown with white carbons and the water molecules as red spheres. The binding sites for piracetam consist of two sets of three distinct sites labeled Binding Sites 1 through 3. Subsites A, B/B′, and C/C′, described previously,37 are shown as circles. The structure is rotated by 90° to illustrate the position of the C/C′ subsites and Piracetam Site 3. Coloring of the backbone is the same as Figure 1.