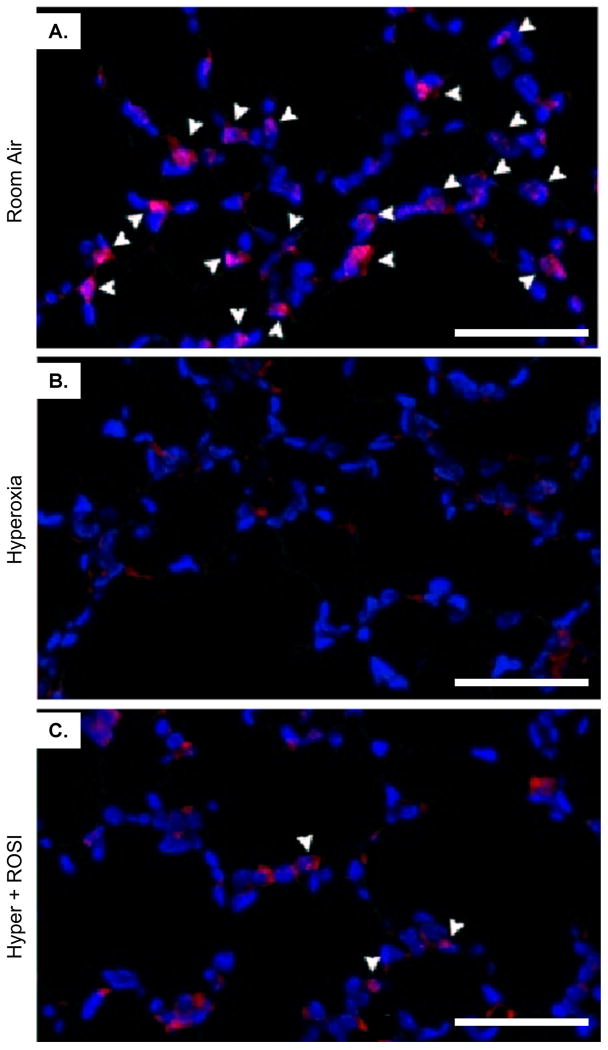
Figure 2. Nuclear Detection of PPAR-γ is Significantly Decreased in Lung Parenchymal Cells Following Neonatal Hyperoxic Exposure.
Fluorescent immunostaining was performed to localize PPAR-γ expression on P13 at RA, in response to hyperoxic exposure and HE+ROSI. On P13 PPAR-γ protein expression was detected in nuclei of parenchymal cells adjacent to type II cells in the alveoli in the RA group (A). Expression was decreased in the hyperoxic exposed (B) and HE+ROSI (C) groups. PPAR-γ reactivity appeared pink indicated by arrow. Nuclei are DAPI stained and appear blue. Scale bar=50uM.