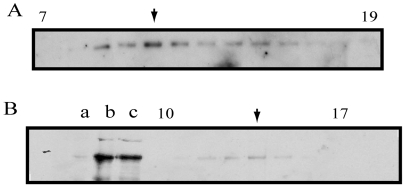
Fig. 3.
Biochemical analysis of native Pav-KLP from Drosophila embryo extract. (A) Fractions 7-19 from 5-20% sucrose density gradient probed by anti-Pav-KLP immunoblotting. The predominant peak (arrow) corresponds to the dimer form. There is a second peak (arrow in B), which could correspond to a monomeric form of Pav-KLP, subject to future investigation. (B) Immunoblotting of embryo MTs and gel filtration fractions probed with anti-Pav-KLP. Lanes: a, Drosophila high-speed supernatant (HSS); b, AMPPMP-MT pellet; c, ATP plus 300 mM KCl eluate of AMPPNP-MTs; gel filtration fractions 10-17 containing Pav-KLP.