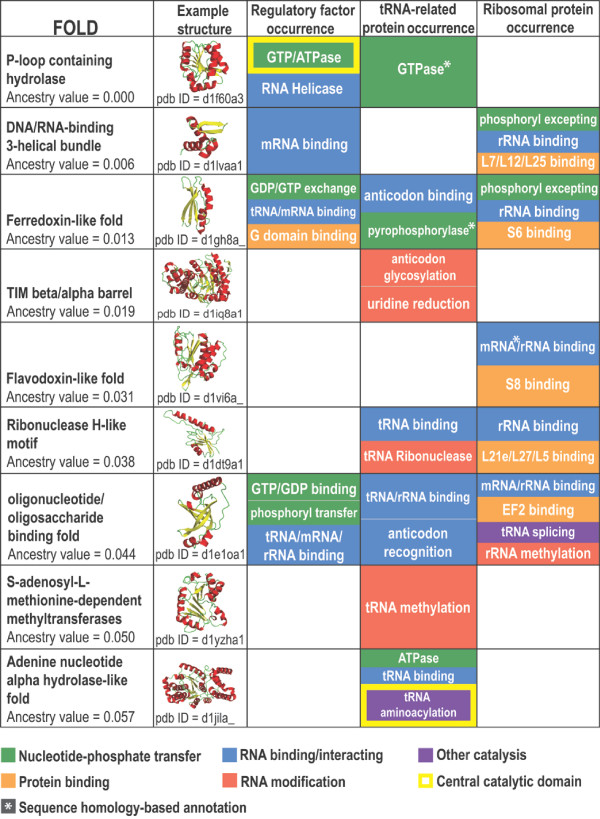
Figure 3.
A summary of functional annotation of the most ancestral translation protein folds. Nine of the ten most ancestral folds identified by Wang et al. [26] are present in translation proteins. The specific functional roles of these folds converge on four general categories: high energy phosphoryl transfer, RNA modification, RNA binding, and protein binding. Exceptions are aminoacylation by tRNA synthetase and tRNA splicing by ribosomal protein S28e. Taken together, the functions imparted by these nine most ancestral folds represent all of the central protein functions in the modern translation system (Figure 4). A summary of the genes in which these folds are found is available as Additional file 2. A detailed annotation of functions imparted by these folds is available as Additional file 3.