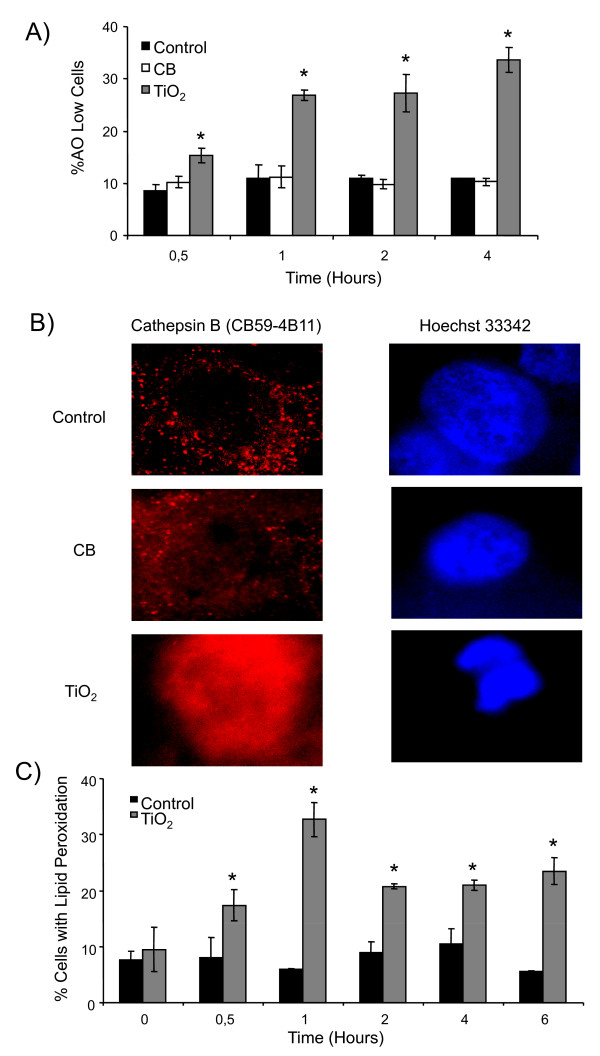
Figure 4.
Distinct apoptotic pathways in 16HBE14o- cells after CB and TiO2 NP exposure: role of lysosomal destabilization and lipid peroxidation. A) Time course study (0.5-4 hours) of acridine orange loading of lysosomes by flow cytometry. Cells were preloaded with acridine orange (0.5 μg.mL-1) for 30 minutes, treated with CB or TiO2 at 20 μg.cm-2 and analyzed by flow cytometry to determine the % of cells with a low AO staining. B) Immunofluorescent detection of release of lysosomal protease (cathepsin B) from destabilized lysosomes after 4 hours of exposure to NPs at 20 μg.cm-2. Cells were stained with monoclonal antibodies against cathepsin B (CB59-4B11). Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342. Representative images of a cell undergoing apoptosis after treatment with CB and TiO2 NPs (×1000). C) Induction of lipid peroxidation. Cell were preloaded with 10 μM Bodipy fluorophore for 30 minutes, exposed to NPs for 0-6 hours at 20 μg.cm-2 and analysed by flow cytometry to determine the % of cells with lipid peroxidation. Data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Representative result of three independent experiments. * statistically different from control p < 0.05 (two tailed).