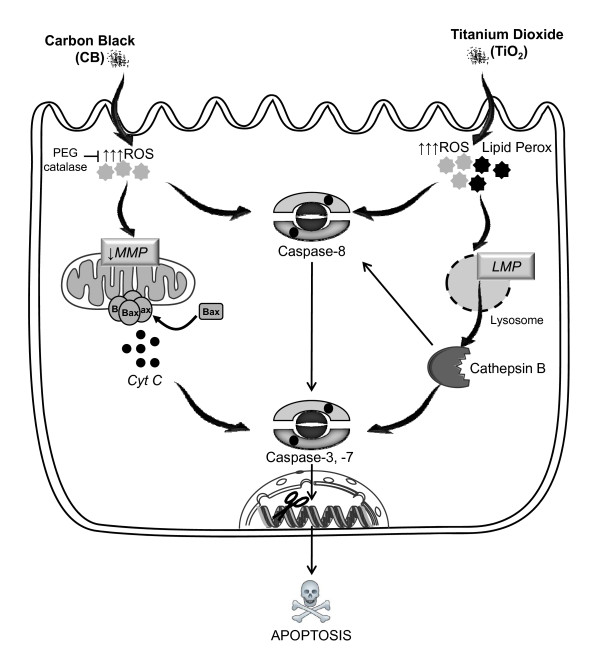
Figure 8.
Schema of the hypothetic pathways of cell death induction by CB and TiO2 NPs in bronchial epithelial cells. CB NP induce apoptosis by a ROS dependent mitochondrial pathway involving loss of MMP, activation of bax and release of cytochrome c resulting in activation of caspases and subsequent DNA fragmentation. TiO2NPs induce cell death through lipid peroxidation and lysosomal membrane destabilization leading to cathepsin B release and subsequent activation of caspases and final apoptotic events. Modulation of oxidative stress by PEG catalase prevents cell death by blocking downstream events only in case of CB NPs. (Image drawn in part using Servier medical art)