Fig. 6.
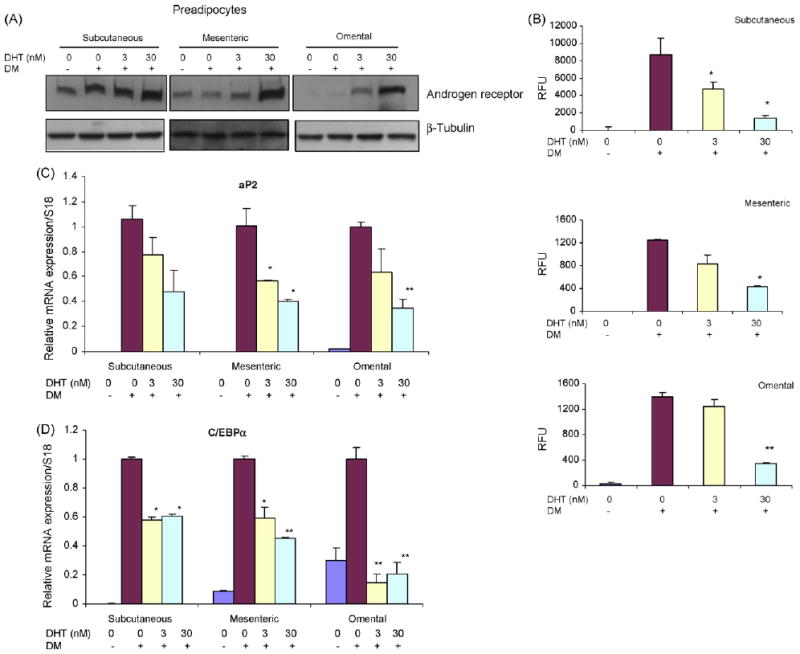
DHT inhibits adipogenic differentiation of human preadipocytes derived from subcutaneous, mesenteric, and omental fat depots. (A) DHT upregulates the expression of AR protein in differentiating preadiopocytes. Preadipocytes were treated with 0–30 nM DHT under differentiating conditions. AR protein expression was assessed by western blot analysis using anti-AR antibody. β-Tubulin serves as protein loading control. (B) DHT inhibits lipid accumulation as assessed by monitoring adipored fluorescence in differentiated human preadipocytes. Following differentiation of preadipocytes derived from subcutaneous (upper panel), mesenteric (middle panel), or omental (lower panel) depot in the presence of 0–30 nM DHT, intracellular triglyceride content was measured by using AdipoRed assay. Data are mean ± S.E.M., n = 6. *P vs. DM control <0.05; **P vs. DM control <0.01. DM, differentiation medium; RFU, relative fluorescence units. (C) DHT downregulates expression of adipogenic differentiation markers. Human preadipocytes derived from subcutaneous, mesenteric, or omental depots were differentiated in the presence of 0–30 nM DHT for 2 weeks. Values are mean mRNA expression levels of adipogenic markers, aP2 (upper panel) and C/EBPα (lower panel) as assessed by RT and real-time PCR using 18S rRNA as an internal control; *P vs. DM control <0.05; **P vs. DM control <0.01.
