Fig. 7.
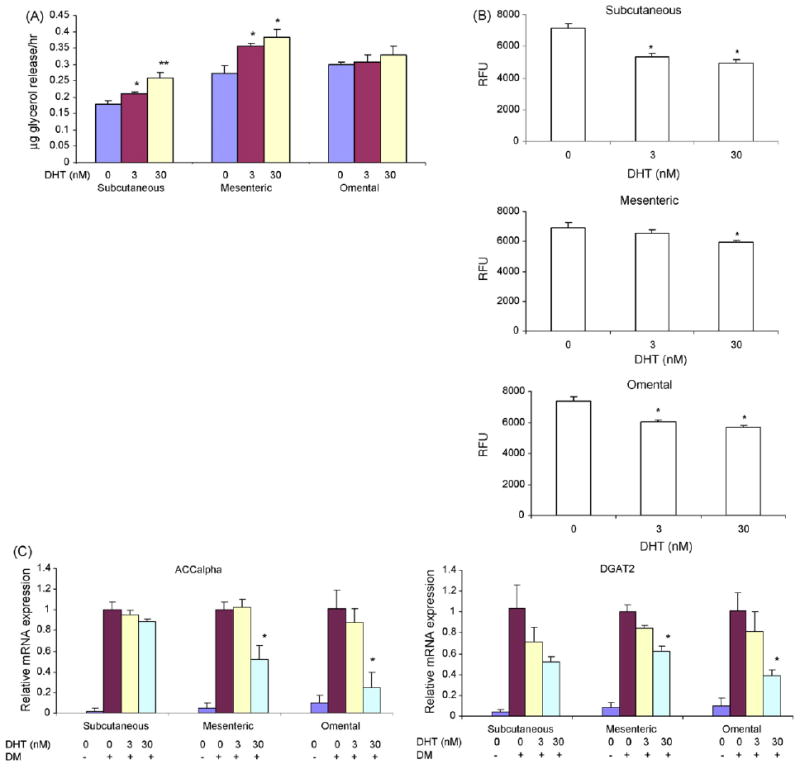
Effects of DHT on lipolysis and fatty acid incorporation into triglycerides in adipocytes differentiated from subcutaneous and mesenteric, and omental preadipocytes. (A) Preadipocytes from subcutaneous (upper panel), mesenteric (middle panel) and omental (lower panel) depots were differentiated in the presence of 0–30 nM DHT. At the end of 2 weeks of differentiation, glycerol release after induction by forskolin was measured in the medium. FSK, forskolin. Data are mean ± S.E.M., n = 4; *P vs. control <0.05; **P vs. control <0.01. (B) DHT inhibits incorporation of BODIPY-labeled fatty acid into triglycerides in adiopcytes derived from hMSCs. hMSCs were differentiated in the presence of 0–30 nM DHT. The cells were then incubated with BODIPY-labeled fatty acid. The incorporation of labeled fatty acid was measured for 2 h. Data are mean ± S.E.M. (n = 5). *P vs. cells treated with insulin <0.05; RFU, relative fluorescence units. (C) DHT downregulates the expression of ACCalpha and DGAT2 mRNA, assessed by qRT-PCR assay, in adipocytes differentiated from human subcutaneous, mesenteric, and omental preadipocytes. Values are mean mRNA expression levels/group as assessed by RT and real-time PCR using HPRT as an internal control; *P vs. medium control <0.05.
