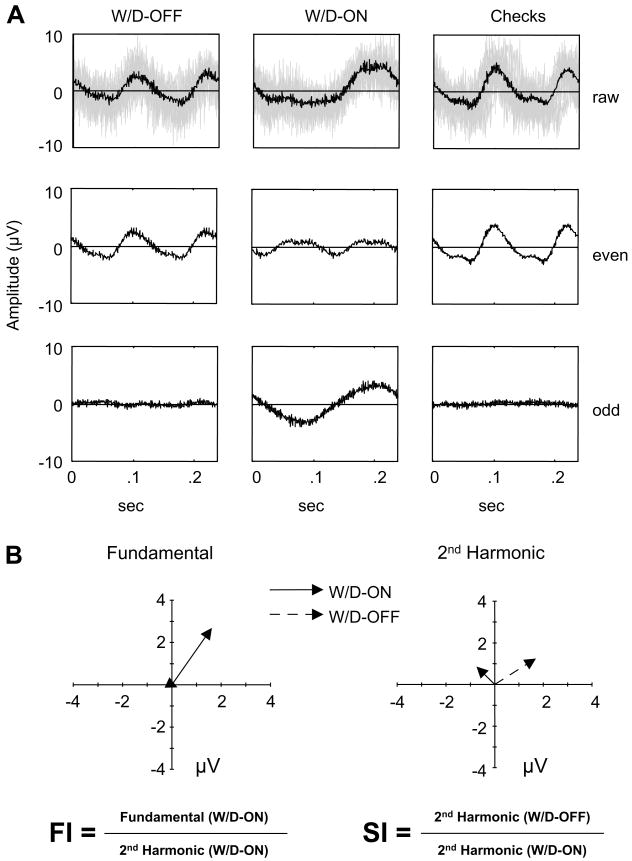
Fig. 2.
(A) VEPs elicited by the windmill/dartboard (W/D-ON and W/D-OFF) and checkerboard stimuli from one normal control (data from Fig. 1B). Averaged waveforms are separated into even and odd harmonic components. Top row: raw signals, middle: even harmonics, bottom: odd harmonics. The light gray shading in the top row indicates the un-averaged EEG traces. (B) Fourier components (fundamental and 2nd harmonic) represented as vectors, whose magnitude indicates amplitude and whose direction indicates response phase. The positive X-axis corresponds to an in-phase response, and counterclockwise rotation corresponds to phase advance.