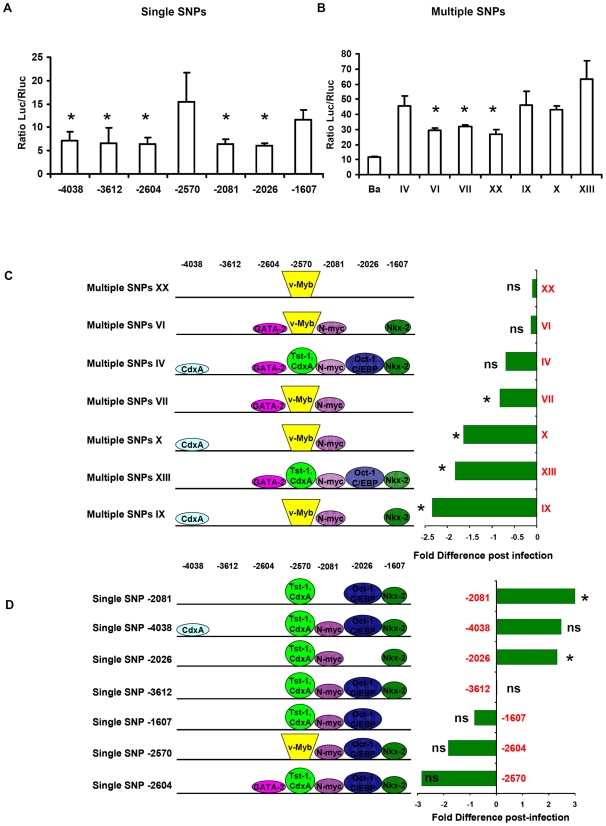
Figure 5. TLR4 promoter GPs common in ABU patients reduce transcription efficiency.
A-B. TLR4 promoter activity determined in a luciferase reporter assay. Human renal carcinoma cells (A498) were transfected with plasmids carrying TLR4 promoter sequences in frame of a luciferase reporter gene. The single SNP promoter constructs contained each of the detected SNPs. The multiple SNP constructs corresponding to GPs in the primary or secondary ABU groups. Luciferase levels were compared to GPIV, which was most common in the population and unrelated to UTI susceptibility. All transfected cells showed increased promoter activity compared to the background (Ba) control (means of three independent experiments, mean+/− SEMs). C-D. Change in promoter activity after infection with the uropathogenic E. coli strain CFT073 and schematic diagram showing possible transcription factor binding sites. The change in promoter activity after E. coli CFT073 infection is shown relative to the GPIV control. The histogram shows the fold difference in promoter activity post-infection for ABU-associated GPs and for the corresponding single SNPs. SNPs VII, X, XIII and IX significantly reduced promoter activity in response to infection. SNPs -2081 and -2026 significantly increased luciferase activity while -2604 and -2570 reduced the response to infection. (* = significant, ns = not significant, compared to uninfected cells carrying the same plasmids, Student T test).