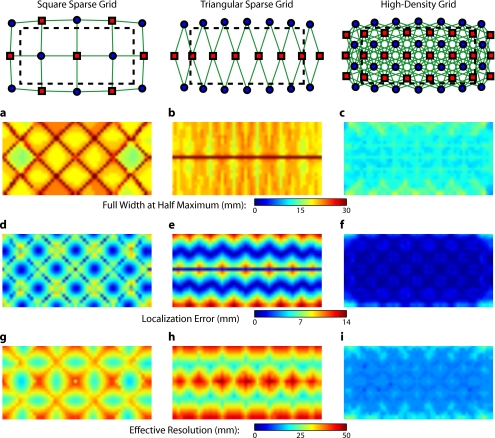
Figure 4.
Image quality metrics for the point-spread functions of targets placed at every location in sparse and high-density grids. (a) to (c) Full width at half maximum of the imaging arrays. The FWHM was defined as the maximum separation of all pairs of points above half maximum contrast. For the sparse arrays, there is overall poor resolution (high FWHM) with worse resolution along lines of symmetry in the grid geometry. Also, note that the triangular array has the worst resolution directly beneath the source line, where the system cannot constrain the activation vertically. The resolution for the high-density array is high across the entire imaging domain with little variation. (d) to (f) Localization error of the imaging arrays. The localization error was defined as the separation between the known target location and the centroid of the voxels reconstructed above half-maximum contrast. While the sparse arrays have low localization error directly under measurements and along points of symmetry, between measurements, it is high. Localization error for the high-density array is uniformly low across the entire field of view. (g) to (i) Effective resolution of imaging arrays. The effective resolution was defined as the diameter of the circle centered at each target position needed to enclose the response. The sparse arrays have poor effective resolution between the measurements, and only good effective resolution directly between adjacent sources and detectors. Effective resolution for the high-density array is good across the entire imaging domain, with little variation.