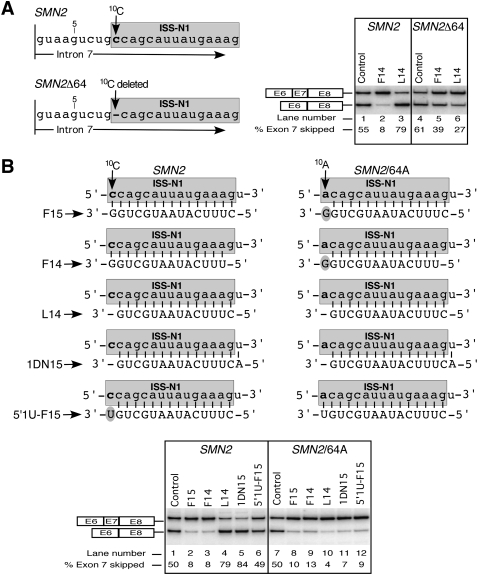
FIGURE 3.
Sequestration of 10C decides the outcome of antisense response. Numbering of nucleotides starts from the first intronic position. ISS-N1 sequence is highlighted in gray. The first C residue in ISS-N1 is marked as 10C. (A) Diagrammatic representation of the 5′ portion of intron 7 of SMN2 minigene and its mutant, SMN2/Δ64. The location of 10C and its deletion are indicated. Effect of ASOs on splicing of wild-type and mutated SMN2 minigene is shown on the right. Cotransfections and analyses were done as in Figure 2A. (B) Diagrammatic representation of wild-type and mutated ISS-N1 targeted by different ASOs. Sequences of ASOs and their base pairing with the corresponding target are shown. Note that wild-type and mutated ISS-N1 element are located within intron 7 of SMN2 and SMN2/64A minigene, respectively. Arrows mark 10C and 10A positions. The 3′-overhang of ASOs are highlighted. Effect of ASOs on splicing of SMN2 minigene and its mutant, SMN2/64A, is shown in the bottom panel. Cotransfections and splicing analyses were done as in Figure 2A.