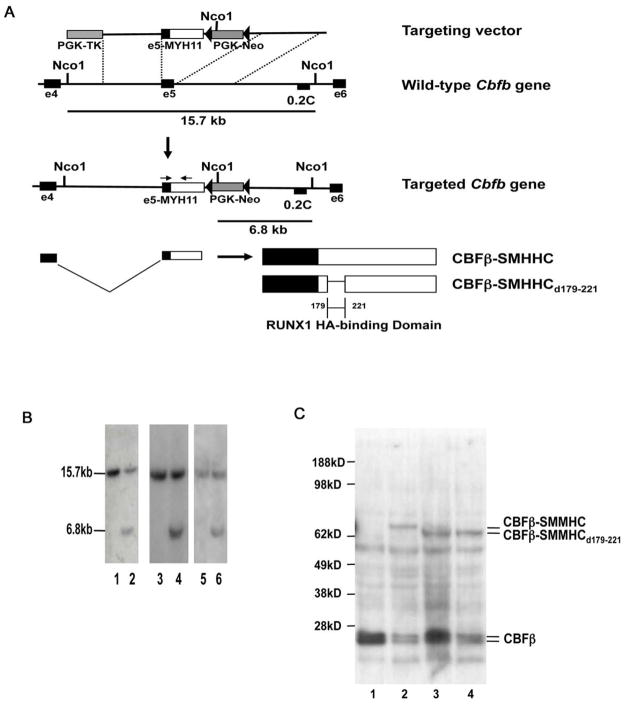
Figure 2. Generation of mouse ES cell lines with Cbfb-MYH11d179-221 and full length Cbfb-MYH11 knock-in constructs.
(A) Targeting strategy used to replace exon5 of Cbfb with the targeting constructs. Location of probe 0.2C and the sizes of NcoI fragments detected by 0.2C are indicated. The arrows indicate the locations of PCR primers used for genotyping. Filled triangles represent lox-P sites.
(B) Southern blot hybridization of NcoI-digested DNA from the parental ES cells (TC1; lanes 1, 3, and 5) and the targeted ES cell clones (lane 2: clone #10 for Cbfb-MYH11; lanes 4 and 6: clones #220 and #269 for Cbfb-MYH11d179-221) with probe 0.2C. The 15.7 kb band corresponds to the wild-type Cbfb allele and the 6.8 kb band corresponds to the knock-in allele.
(C) Western blot analysis of ES cells. Lane 1: the parental ES cell line TC-1; Lane 2: ES cell line #10 (knock-in of full-length Cbfb-MYH11), Lanes 3 and 4: ES cell lines #220 and #269 with knock-in of Cbfb-MYH11d179-221. The antibody used was the mouse monoclonal antibody (β141.2) specific for CBFβ. The calculated molecular weights for CBFβ-SMHHC, CBFβ-SMHHCd179-221, and CBFβ are 71 KD, 65 KD, and 22 KD, respectively.