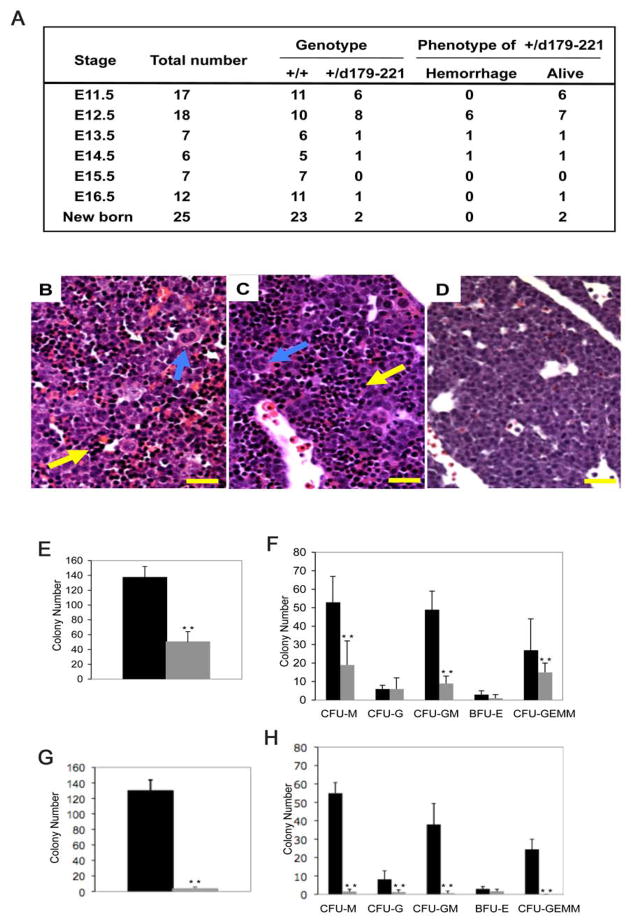
Figure 3. Partial phenotypic rescue in Cbfb+/MYH11d179-221 heterozygous embryos.
(A) Genotype and phenotype of embryos derived from crosses between Cbfb–MYH11 chimeras and normal females. +/+ are wild type littermates, +/d179-221 are embryos heterozygous for Cbfb-MYH11d179-221 knock-in. Viability was determined by embryo heart beats.
(B–D) Histologic sections of fetal livers from E12.5 embryos. (B) wildtype control, (C) Cbfb+/MYH11d179-221, (D) Cbfb+/MYH11. Sections were stained with H and E. Yellow arrows indicate hematopoietic cells in the livers. Blue arrows indicate megakaryocytes. Scale bars represent 100 μm.
(E–H) In vitro differentiation assay of fetal liver hematopoietic cells. Panels (E) and (F) compare colony numbers from embryos of wildtype (black bars) and Cbfb+/MYH11d179-221 (gray bars). Panels (G) and (H) compare colony numbers from embryos of wildtype (black bars) and Cbfb+/MYH11 (gray bars). Panels (E) and (G): total colony numbers. BFU-E: burst-forming unit-erythroid; CFU-E: colony-forming unit-erythroid; CFU-G: colony-forming unit-granulocyte; CFU-GM: colony-forming unit-granulocyte/macrophage; CFU-GEMM: colony-forming unit-granulocyte/erythroid/macrophage/megakaryocyte; CFU-M: colony-forming unit-macrophage. The error bars represent one standard deviation. **: P<0.001