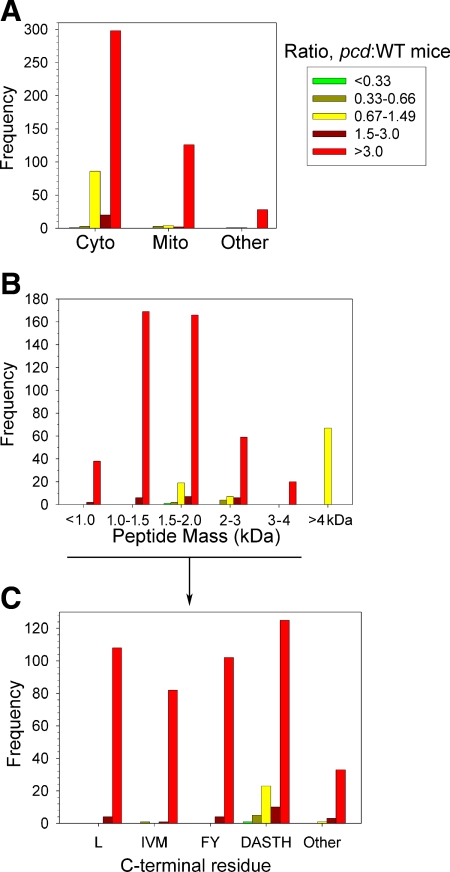
Figure 3.
Summary of quantitative peptidomics results. All identified peptides were divided into 5 categories: greatly decreased in pcd mice compared to WT (pcd:WT ratio<0.33); slightly decreased (pcd:WT ratio 0.33–0.66); peptides that are present in roughly equal levels in pcd and WT brains (pcd:WT ratio 0.67–1.49); peptides that are slightly increased in pcd mice (pcd:WT ratio 1.5–3.0); and greatly increased in mutants (pcd:WT ratio>3.0). The y-axes indicate number of lines of Supplemental Table 1 that match each category (each line of Supplemental Table 1 represents a peptide in an LC/MS run). A) Subcellular location of protein precursor of peptides. Cyto, cytosol; Mito, mitochondria; other, includes nucleus, lysosomes, and plasma membrane. B) Peptides derived from cytosolic, mitochondrial, and other nonsecretory pathway proteins were divided into the indicated mass ranges. C) Analysis of the C-terminal residues of the <4-kDa peptides from cytosolic, mitochondrial, and other nonsecretory vesicle proteins. To provide a larger n for each group, several similar amino acids were pooled in this analysis. Leu constituted a large enough group to be analyzed individually. Pools of data included aliphatic (Ile, Val, Met), aromatic (Phe, Tyr), some small and/or polar side chain (Asp, Ala, Ser, Thr, His), and other residues (Gly, Asn, Gln, Cys, Glu, Lys, and Arg). Neither Trp nor Pro was detected in the C-terminal position in any of the observed peptides, so these residues could not be included in the analysis.