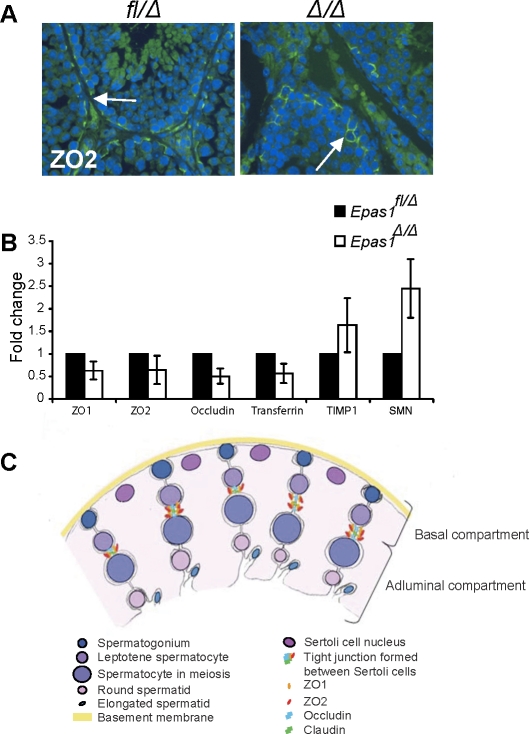
FIG. 9.
Tight junction proteins are affected in Epas1Δ/Δ testes. A) ZO2 protein was still detected by IF in both control and Epas1Δ/Δ testes (arrows, original magnification ×400). B) The mRNAs encoding ZO1, ZO2, occludin, and transferrin were somewhat decreased in Epas1Δ/Δ testes. In contrast, the protease inhibitor TIMP1 and SMN (reflecting the myoid cell phenotype) were slightly increased in Epas1Δ/Δ mice (n = 4). Changes in relative abundance of these transcripts were not statistically significantly; however, all four mutant animals clearly displayed a trend toward decreased expression of each gene. C) Schematic drawing showing the different cell types, junctions, and compartments present in the seminiferous tubules. Sertoli cell nuclei (dark pink) are located close to the basement membrane (yellow), but their cytoplasm (light pink) reaches down to the lumen and connects with other Sertoli cells and germ cells. Tight junctions are formed between two Sertoli cells via ZO1, ZO2, occludin, and claudin interaction and divide the seminiferous tubule into a basal and adluminal compartment. Germ cells move toward the lumen as they mature. Spermatogonia (dark blue) are attached to the basement membrane. Once germ cells enter meiosis, they have passed the BTB and are now separated from blood and lymph. Mature spermatozoa are released into the lumen (light blue).