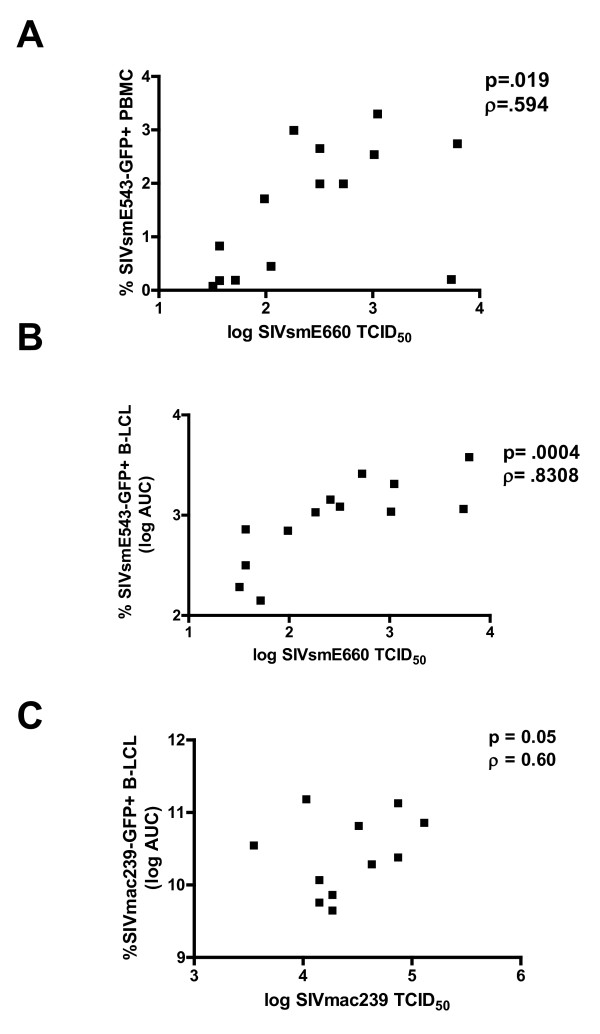
Figure 3.
Positive correlation between rhesus monkey PBMC susceptibility to infection with wild type SIVsmE660 and a single cycle VSV-G pseudotyped SIVsmE660-GFP construct. (A) PBMC susceptibility to SIVsmE660 replication was defined by TCID50, and SIVsmE543-GFP infection was defined as % GFP+ PBMC following infection with VSV-G pseudotyped SIVsmE660-GFP determined using flow cytometric analysis. (B) Positive correlation between rhesus monkey PBMC susceptibility to SIVsmE660 infection, as defined by TCID50, and area under the curve (AUC) of % GFP+ B-LCL following infection with serial dilutions of VSV-G pseudotyped SIVsmE543-GFP. (C) Positive correlation between rhesus monkey PBMC susceptibility to SIVmac239 infection, as defined by TCID50, and area under the curve (AUC) of % GFP+ B-LCL following infection with serial dilutions of VSV-G pseudotyped SIVmac239-GFP.