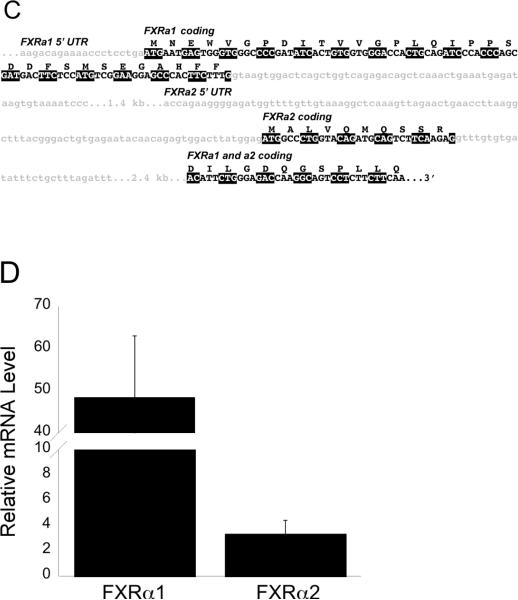
Figure 1. A: Protein sequences of medaka FXRα1 and FXRα2.
A gray box denotes the differences between the two isoforms as a result of alternative splicing. B: Fxrα1 and Fxrα2 have different 5' ends due to alternative splicing. As shown here, differential splicing results in the formation of these two isoforms. Gray shading indicates the 5'UTR for each gene. No shading indicates their coding regions. Exons with the same number indicate those that are identical in both Fxrα isoforms. C: Further details on splicing differences between Fxrα isoforms. Light gray shaded, lower case letters indicates noncoding regions. Coding regions for each isoform are specifically marked and denoted in upper case letters. Codons are highlighted alternatively in black and white for clarity. Fxrα2's start codon is downstream of Fxrα1's and is located in a predicted (Ensembl) Fxrα1 intron. D: Relative Fxrα1 and Fxrα2 levels in male liver. N=5, normalized to 18S RNA levels.