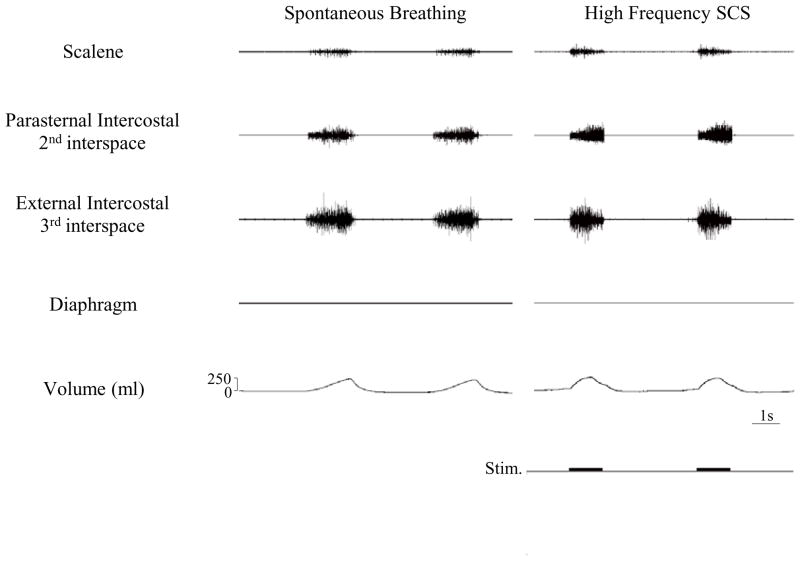
Figure 1.
Multiunit EMGs of the scalene, parasternal intercostal, external intercostal and diaphragm muscles during spontaneous breathing (left panel) and during HF-SCS (right panel). Stimulus parameters during HF-SCS were adjusted to approximate inspired volumes during spontaneous breathing. Consequent to phrenicotomy, diaphragm EMG was silent. As with spontaneous breathing, HF-SCS results in an asynchronous EMG pattern.