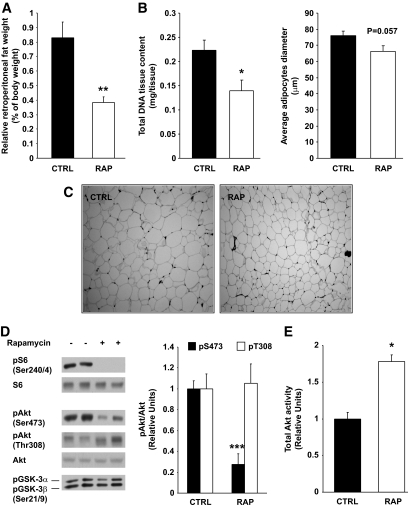
FIG. 1.
Chronic rapamycin treatment decreases adiposity. Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with vehicle or rapamycin (2 mg/kg/day) for 15 days. A: Relative retroperitoneal fat weight. Total DNA tissue content and adipocyte diameter (μm) (B) and representative images of retroperitoneal fat (C) from control and rapamycin-treated rats (magnification ×10) D: Representative Western blots of adipose tissue lysates are shown for phosphorylated S6 (Ser240/244), Akt (Ser473 and Thr308), GSK-3α/β (Ser21/9), and total proteins (two representative animals of six). The graphs depict densitometric analysis of normalization of phospho-Akt/Akt protein. E: Adipose tissue proteins (500 μg) were immunoprecipitated with total Akt antibody. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed for Akt activity. The graphs depict densitometric analysis of total Akt activity. n = 6 for each group. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. CTRL, control; RAP, rapamycin.