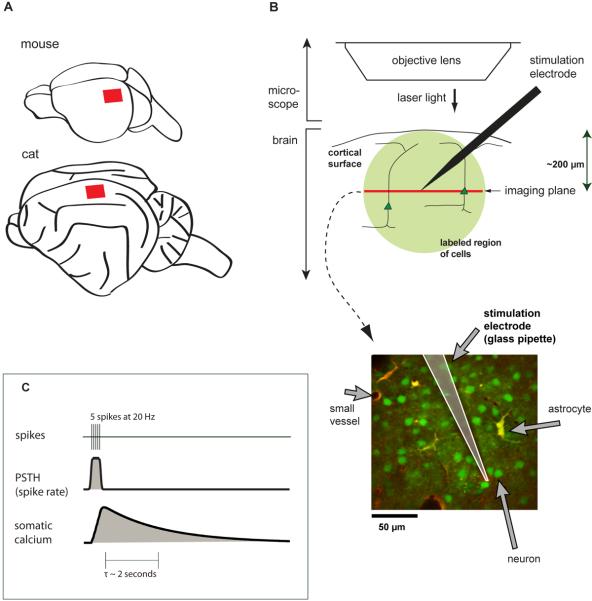
Figure 1. Using two-photon imaging to measure the effects of cortical microstimulation.
(A) Schematic location of imaging sites in cortex, primary visual cortex of mouse, rat (not shown), and cat (area 18).
(B) Two-photon bulk-loaded calcium imaging in vivo. Femtosecond-pulsed laser light is used to measure calcium-induced fluorescence changes in neurons. A single plane is imaged at one time. Lower panel: example image. All cells are loaded with OGB-1 AM (green), and astrocytes are labeled with SR101 (red/yellow).
(C) Relationship between calcium concentration and spiking activity. Top: a simulated train of 5 spikes. Middle: spike rate, computed by smoothing the spike train with a Gaussian kernel. Bottom: expected somatic calcium concentration, computed by convolving an exponential describing calcium influx with the spike train.