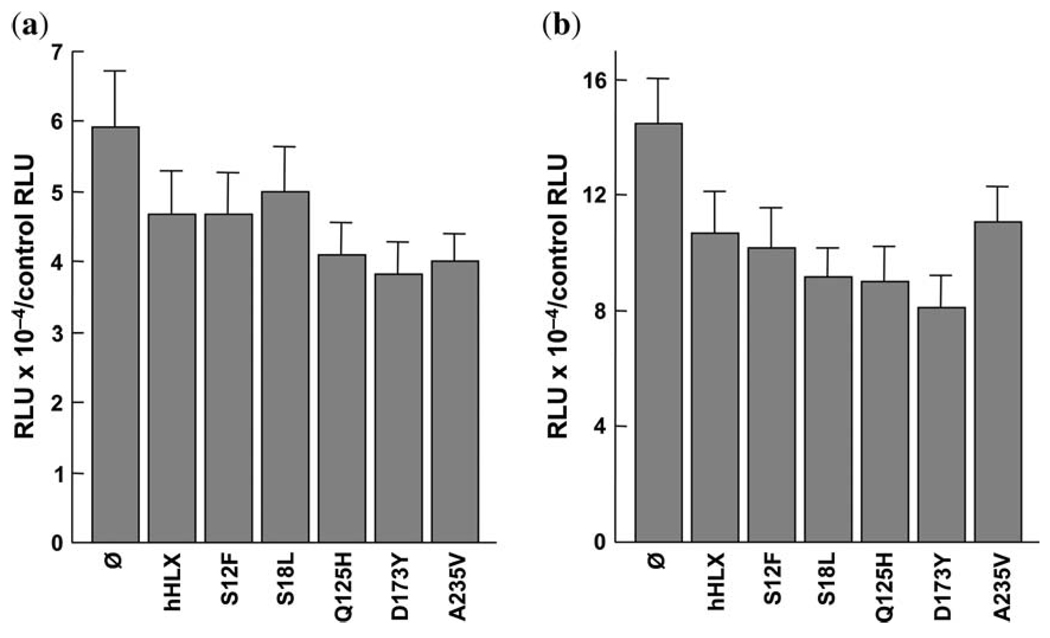
Fig. 4.
Functional studies of the ability of wild-type Hlx and Hlx constructs with sequence variants to induce α-smooth muscle actin and SM22α promoter activity in a cell line derived from an Hlx−/− mouse. (a) The results for the α-smooth muscle actin promoter are shown. The x-axis has bars representing the different sequence variants and the y-axis has the values for ratios of firefly luciferase (expressed by pGL3 constructs with promoters of interest, expressed in relative luciferase units, or RLUs) to Renilla luciferase (expressed by pRL-SV40) for triplicate wells in duplicate experiments. (b) The results for the SM22α promoter are shown. The x-axis has bars representing the different sequence variants and the y-axis has the values for ratios of firefly luciferase (expressed by pGL3 constructs with promoters of interest, expressed in RLUs) to Renilla luciferase (expressed by pRL-SV40) for triplicate wells in duplicate experiments.