Figure 1. Misrepair of DNA breaks cause chromosomal translocations[rk4].
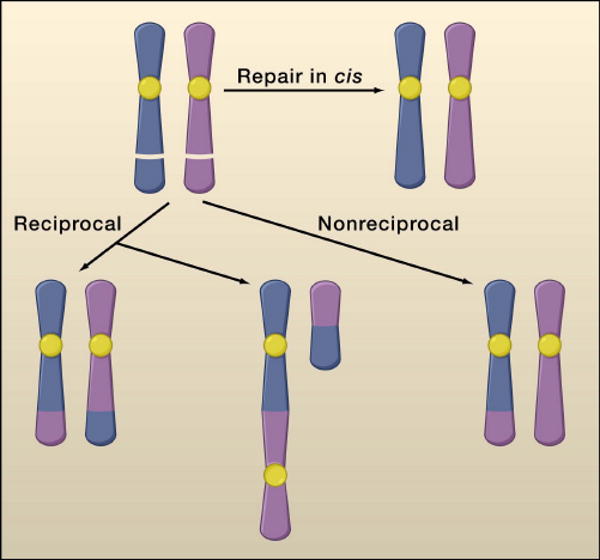
Chromosomal translocations require formation of paired double strand DNA breaks (DSBs) on different chromosomes. DSBs can be repaired in cis, or can result in chromosomal translocation by rearrangement between non homologous chromosomes. Depending on the topology of the rearrangement, the translocation can be reciprocal (balanced or unbalanced) or non-reciprocal. The majority of translocations associated with cancer in human lymphoid tumors involve balanced chromosomal translocations, whereas epithelial cancers usually carry complex nonreciprocal translocations.
