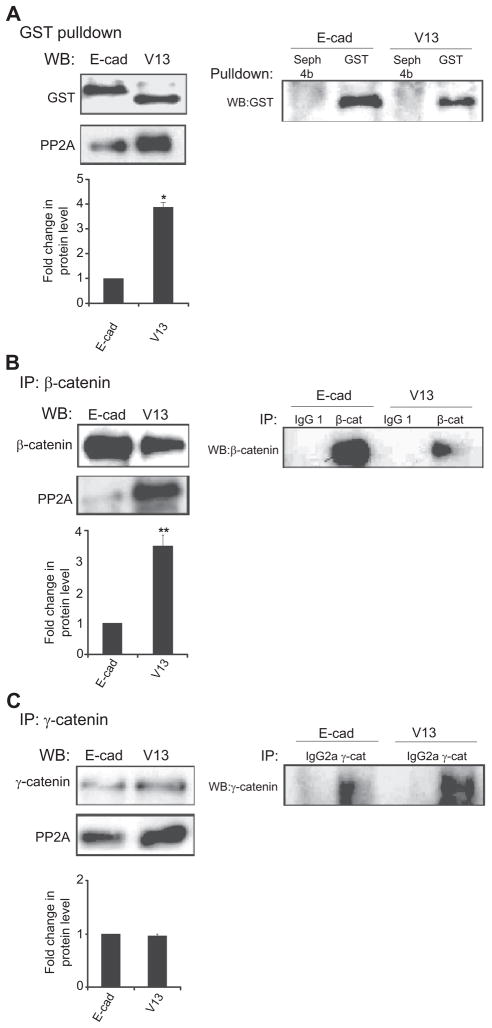
Figure 2.
PP2A preferentially associates with β-catenin in V13-transfected cells. (A) The hypoglycosylated variant V13 (V13) recruits more PP2A than wild-type E-cadherin (E-cad). Left panel, GST pulldown samples from CHO cells transfected with either E-cad or V13 were assessed for association with PP2A by Western blot (WB). Bargraph, Fold change of PP2A protein level from V13 cells was determined in comparison with E-cad cells after normalization to GST (*P < 0.05). Right panel, Controls for specificity of GST pulldown. (B) PP2A preferentially binds to β-catenin complexes. Left panel, WB of PP2A in β-catenin immunoprecipitates. Bar graph, Fold change in PP2A levels in V13 cells was determined in comparison with the E-cad cells in β-catenin immunoprecipitates after normalization to β-catenin (**P < 0.01). Right panel, Isotype controls for specificity of β-catenin immunoprecipitates. (C) N-glycosylation of E-cadherin does not affect the binding of PP2A to γ-catenin complexes. Left panel, WB of PP2A in γ-catenin immunoprecipitates. Bargraph, Fold change in PP2A levels in V13 cells was determined in comparison with the E-cad cells in γ-catenin immunoprecipitates after normalization to γ-catenin. No significant change in its association with the γ-catenin complexes was detected. Right panel, Isotype controls for specificity of γ-catenin immunoprecipitates. Error bars represent standard deviation from three independent experiments; P values were calculated by two-tailed t-test.