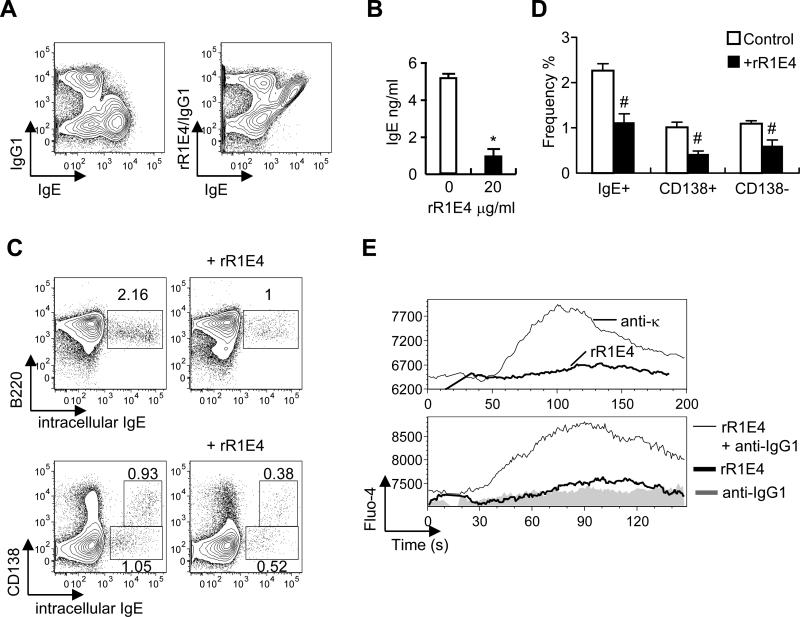
Figure 4.
Ability of recombinant R1E4 (rR1E4) anti-IgE protein to affect the biological responses of IgE+ B cells generated in tissue culture.
(A) BALB/c spleen cells were induced to undergo IgE class switch by culture at 2×105 cells/ml for 4 days with IL-4 (25 ng/ml) and anti-CD40 (10μg/ml); binding by rR1E4 was examined. Right panel shows staining with rR1E4 (10μg/ml) followed by FITC anti-mouse IgG1 and Alexa647 anti-IgE (EM95). (B,C,D) Spleen cells (2×105 cells/ml) were stimulated for 4 days with IL-4 (25 ng/ml) and anti-CD40 (1μg/ml) with or without 20μg rR1E4. (B) IgE levels in culture supernatants on d4 as measured by ELISA. (C) Analysis of IgE+ B cell and IgE+ plasma cell frequencies at d4 of culture, as determined by staining for intracellular IgE, B220 and CD138. (D) Summary of rR1E4-induced changes in IgE subpopulations, as shown in C. (E) rR1E4-induced calcium flux in fluo-4 loaded B cells recovered at d4 of culture. Top panel, B cells were treated with either anti-Igκ or rR1E4 alone. Lower panel, cells were precultured with anti-IgG1 alone for 30 min (to obscure the response of IgG1 cells) then stimulated with either anti-IgG1 or rR1E4, which is super-crosslinked by free anti-IgG1. Results presented in B and D represent the means and standard deviations of 4 separate experiments. *P < 10-4, #P < .05.