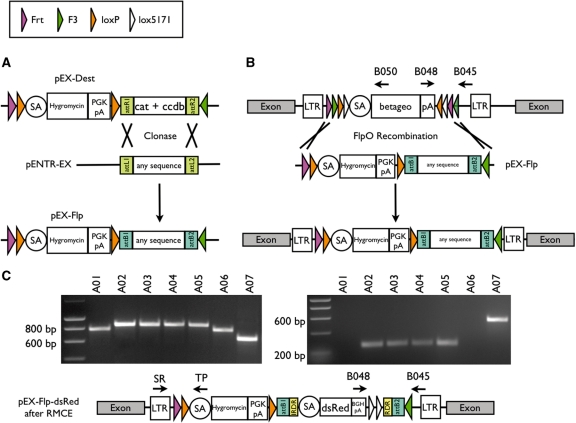
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic outline of the procedure for individual modification and use of pEX-FLP. Any DNA sequence, which is cloned between the attL1/2 recombination sites in the pENTR-EX, can be exchanged with an attR1/2 flanked cat ccdb cassette of pEX-Dest in vitro. (B) Schematic illustration of the FLPo RMCE in ES cells. pEX-FLP harbors two heterospecific flippase recombination sites, therefore cotransfection of FLPo and pEX-FLP to any FlEx gene trap ES cell clone allows replacement of β-geo cassette. (C) Analysis of successfully exchanged locus with pEX-FLP-dsRed containing a adSA-dsRed-BGHpA sequence flanked by IR/DR of Sleeping Beauty transposase. A representative PCR screen of seven hygromycin resistant clones (E307D01 derivates, A01–A07) concerning orientation of the genetrap vector and successful exchange (left: primers B045, B048 and B050; right: primers SR, TP). A01 and A06 are inverted β-geo insertions and show an 800-bp band on the left and no band on the right. A02–A05 are successfully exchanged clones and show an 839-bp band on the left and the small 239-bp band on the right. Clone A07 carries the original β-geo insertion and gives rise to the 631-bp band on the left and the 516-bp band on the right.