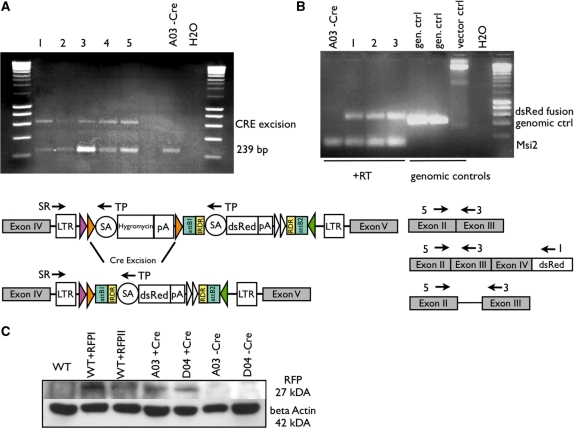
Figure 3.
(A) Removal of hygromycin resistance upon Cre activity. Cre-transfected exchange clone A03 (E307D01/pExFLP-dsRed derivative) was analysed using primers located within both the hygromycin/dsRed cassettes (TP) and the LTR of the original gene trap vector (SR). PCR on total genomic DNA of five pooled transfected dishes (lanes 1–5) compared to genomic DNA of clone A03 before Cre transfection (A03 −Cre). The internal primer (TP) gives rise to the larger product (619 bp) after successful excision of the hygromycin cassette. Before hygromycin excision, primer TP amplifies a smaller product of 239 bp. (B) RT-PCR and triple PCR analysis to determine splicing to the dsRed after hygromycin excision by using external primers in exon II (5) of the insertion locus (Msi2) and an internal dsRed primer (I) and as internal wild-type control a primer located in exon III (3) of the Msi2 gene. cDNA of individual clones derived from Cre-transfected clone A03 after puromycin selection (lanes labelled 1–3) compared to cDNA of clone A03 before Cre transfection (lane A03 −Cre). As control genomic DNA of two gene trap clones (E307D01 and E326E12) and pEX-FLP-dsRed plasmid was used. (C) Western blot analysis of protein extracted from ES cells probed with a polyclonal RFP antibody. As controls wild-type ES cells either untransfected (WT) or transiently transfected with two different dsRed expression plasmids (WT + RFPI + II) were used. Exchange clones A03 and D04 were analysed prior (−CRE) and after (+CRE) transient CRE transfection. DsRed protein positive samples show a 27-kDa band. Lower blot shows loading control with beta actin monoclonal antibody (42 kDa).