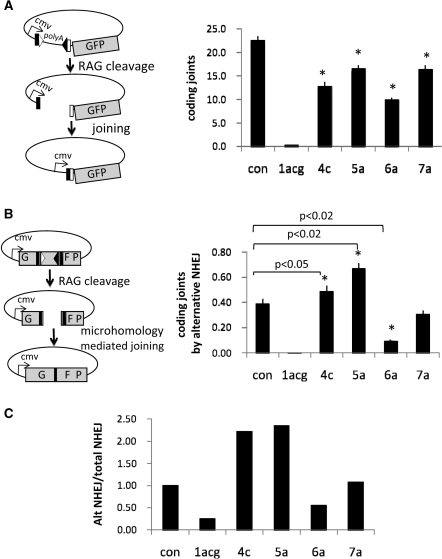
Figure 3.
Certain non-consensus RSS alter handling of CEs after cleavage. (A) Schematic diagram of GFP reporter construct. GFP is under the control of the CMV promoter. RAG cleavage and subsequent coding joint formation deletes a poly-adenylation site located upstream of the GFP, thereby allowing GFP expression. Right panel shows quantification of FACS data for coding joint formation (n = 5, *P < 0.02). RMP41 cells were transiently transfected with full-length RAG proteins and a fluorescent reporter for coding joint formation, 290-GFP containing either a consensus pair of RSS or a non-consensus 12RSS, as indicated. (B) Alternative NHEJ assay (n = 5). Cleavage by the RAG proteins followed by resection of 10 nts from each CE reveals a nine-nucleotide microhomology used to direct the precise repair of the GFP gene. Highly deleted coding joints that use microhomologies are characteristic of joining by the alternative NHEJ pathway. Right panel shows coding joint formation by alternative NHEJ assay as measured by transient transfection of RMP41 cell with full-length RAG proteins using ALT-GFP reporter substrate containing either a consensus pair of RSS or a non-consensus 12RSS, as indicated. (C) Ratio of alternative NHEJ to total NHEJ, normalized to one for a consensus pair of RSS. Similar results were obtained with core RAG2 (data not shown).