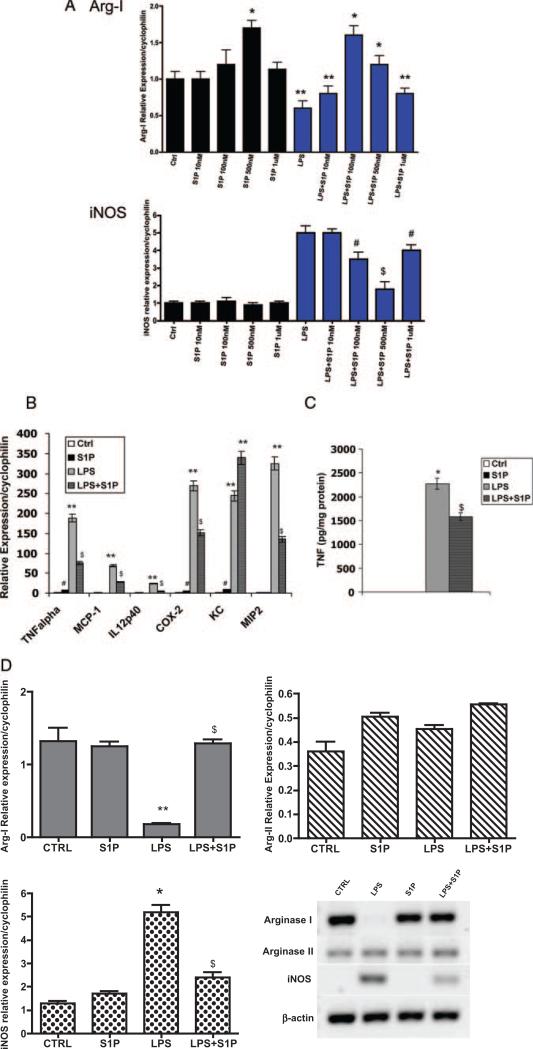
Figure 2.
S1P reduces LPS-induced inflammatory gene expression. A, S1P dose response. Total RNA was isolated from C57BL/6J peritoneal macrophages treated with S1P at concentrations of 10 nmol/L, 100 nmol/L, 500 nmol/L, and 1 μmol/L in the absence (black bars) or presence (blue bars) of 10 ng/mL LPS for 4 hours. Quantitative real-time PCR for murine Arg I and iNOS were performed. Cyclophilin was measured as a housekeeping gene for normalization purposes. Data are expressed using the relative expression method using B6 control as set to 1. *P<0.001 vs control (Ctrl), **P<0.0001 vs Ctrl, #P<0.01 vs LPS, $P<0.001 vs LPS by ANOVA. Data are from 3 independent experiments using 4 mice per group. B, Inflammatory gene expression. Cytokine mRNA expression was determined using quantitative real-time PCR. C57BL/6J peritoneal macrophages were treated with media alone (Ctrl) or with 10 ng/mL LPS in the absence or presence of 500 nmol/L S1P for 4 hours. **P<0.0001 vs Ctrl, $P<0.005 vs LPS, #P<0.05 vs Ctrl by ANOVA. C, TNFα secretion. TNFα secretion by C57BL/6J peritoneal macrophages was measured using ELISA. Values were normalized to total cellular protein. *P<0.001 vs Ctrl, $P<0.005 vs LPS by ANOVA. D, Arg I and iNOS expression. Levels of mRNA expression in C57BL/6J peritoneal macrophages were determined using quantitative real-time PCR as described in Materials and Methods and are graphically shown. **P<0.0001 vs Ctrl, $P<0.009 vs LPS, *P<0.001 vs Ctrl by ANOVA. Data represent 5 mice per group performed in triplicate. Conventional RT-PCR products of Arg I, Arg-2, iNOS, and β-actin are also shown in a representative gel.