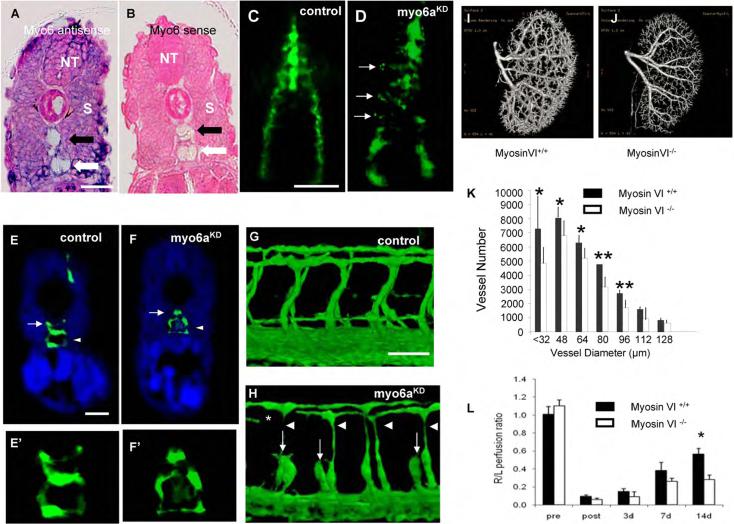
Figure 5. Myo6aKD Impairs Arterial Development in Zebrafish; Functional Effects of Mysosin VI Gene Disruption in Mice.
(A,B) Transverse section through the trunk of a 28 hpf zebrafish embryo stained by whole-mount in situ hybridization using a myo6a specific antisense (A) or sense (B) riboprobe. Myo6a expression was observed in the neural tube (NT), somites (S) and both the dorsal aorta (black arrow) and posterior cardinal vein (white arrow). The observed expression pattern is specific as no signal was observed upon hybridization using the sense probe. (C,D) Dorsal view of 16 hpf Tg(fli1:EGFP)y1 embryo, head on top. In control embryos (C) GFP+ angioblasts migrated in an ordered anteroposteriorly directed zipper-like pattern from the lateral plate mesoderm towards the midline where they assembled into the primitive axial vessels. In contrast, in myo6aKD embryos (D) a portion of angioblasts (arrows) stalled along their lateromedial movement and others failed to maintain their correct stereotyped trajectory, resulting in apparently chaotic migration pattern. (E,F) Transverse sections through the trunk of Tg(fli1:EGFP)y1 embryos of 30 hpf, following a whole-mount immunostaining using an anti-GFP antibody (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue); head on top. Compared to control embryos (E,E'), myo6aKD embryos had a strikingly thinner dorsal aorta (arrow) with an obvious reduced lumen size, while the posterior cardinal vein (arrowhead) remained unaffected (F,F'). E' and F' are magnifications of the axial vessels in panel E and F, respectively. (G,H) Lateral view on a trunk segment of Tg(fli1:EGFP)y1 embryos at 40 hpf; head to the left. In control embryos (G) ISVs sprouted bilaterally from the dorsal aorta adjacent to the ventral somite boundaries and navigated upwards to the laterodorsal roof of the neural tube, where they split, elongated and fused to form the DLAV. However, in myo6aKD embryos (H) ISVs often consisted of slender endothelial cells (arrowheads) and/or stalled along their dorsal trajectory (arrows), thereby impairing proper DLAV formation (asteriks). Scale bars represent 10 μm in panel A,B,E–F' and 5 μm in panel C,D,G,H. See also Fig S3 and S4.
(I,J) Representative reconstructed micro-CT images of whole kidneys (16μm resolution; n=3) from age- and gender-matched (I) myosinVI+/+ and (J) myosinVI−/− mice. Note marked reduction in branching in myosinVI−/− mice.
(K) Quantitative analysis of micro-CT images indicates a marked decrease in total number of <100μm diameter vessels in myosinVI−/− mice (white bars) relative to myosinVI+/+ mice (black bars). (Mean±SEM, * P < 0.05)
(L) Quantitative analysis of laser Doppler images indicates significant alterations in hindlimb reperfusion 14 days after femoral artery ligation in myosinVI−/− mice (white bars) relative to myosinVI+/+ mice (black bars). (Mean±SEM, * P < 0.05)