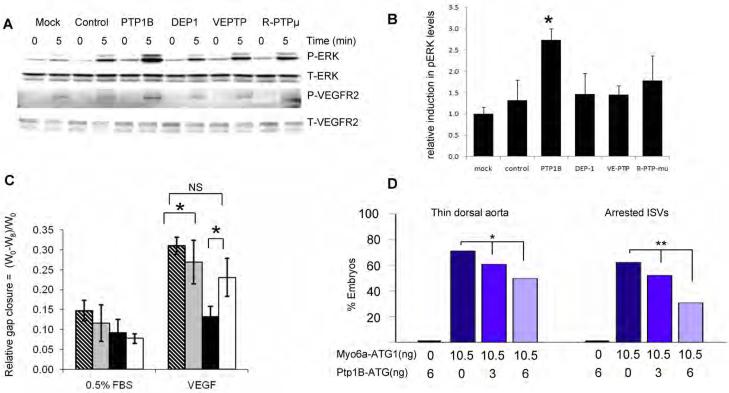
Figure 6. Effect of Phosphatase Knockdown on VEGF signaling.
(A,B) PTP1B knockdown increases VEGF signaling in synectin−/− AEC. Synectin−/− AEC were transfected with the siRNAs indicated for 2 days, starved, and stimulated with 50ng/ml VEGF-A. Western blotting of total cell lysates with pErk and pVEGFR2(Y1175) shows increased phosphorylation after PTP1b knockdown (Panel A), Quantification of pERK activation is shown in Panel B. (Mean±SEM, * P < 0.05). See also Fig S6.
(C) Effect of PTP1B knockdown on AEC migration: The relative distance migrated by AEC from synectin+/+ and −/− mice grown on fibronectin coated dishes was measured 8 hrs following `wounding' of a confluent monolayer and stimulation with 0.5%FBS or 50 ng/ml VEGF-A in the presence of either control siRNA or PTP1b siRNA. Note increased extent of migration of synectin−/− cells in response to VEGF following treatment with PTP1B siRNA. Means +/− SD, * = P<0.05. Stippled bars: synectin+/+ AEC treated with control siRNA; grey bars: synectin+/+ AEC with PTP1b siRNA; black bars: synectin−/− AEC with control siRNA; white bars: synectin−/− AEC with PTP1b siRNA.
(D) Effect of Co-Knockdown of Myo6a and Ptp1b in Zebrafish: Quantitative analysis of arterial defects in morphant embryos revealed that Ptp1b-ATG partially rescues the myo6a knockdown phenotype in a dose-dependent manner. Single ptp1bKD (6ng Ptp1b-ATG) does not induce vascular defects. Dark blue bars indicate single myo6aKD (10.5ng Myo6a-ATG1), blue and light blue bars indicate double ptp1bKD:myo6aKD (10.5ng Myo6a-ATG1 combined with 3 or 6ng Ptp1b-ATG, respectively). *, P<0.05; **, P<0.001.