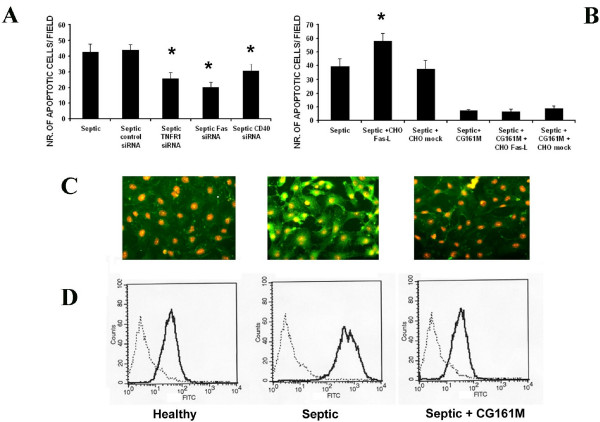
Figure 4.
Protective effect of resin adsorption on septic plasma-induced sensitisation of TEC to death receptor-mediated apoptosis. (a) Evaluation of apoptosis (TUNEL assay) induced by incubation for 48 hours with septic plasma on tubular epithelial cells (TEC) transfected with specific siRNA to knock-down TNFR1, Fas or CD40 expression. The rate of apoptosis was significantly decreased in TEC transfected with all tested siRNA (*P < 0.05 Septic TNFR1 siRNA, Septic Fas siRNA or Septic CD40 siRNA vs. Septic or Septic control siRNA). (b) Sensitization of TEC to plasma-induced apoptosis (TUNEL assay) after incubation with supernatants collected from chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells transfected with a cDNA coding for a soluble form of Fas Ligand (CHO Fas-L) but not with an empty vector (CHO mock) (*P < 0.05 Septic + CHO FasL vs. Septic or Septic + CHO mock). CHO cell supernatants did not influence the apoptotic rate of TEC in presence of plasma pre-adsorbed with the Amberchrom resin. In a and b, data are expressed as average number of green fluorescent apoptotic cells ± standard deviation in 10 different fields (×100 magnification). Analysis of variance with Newmann-Keuls multicomparison test was performed. (c and d) Representative immunofluorescence micrographs (c) and FACS analysis (d) of Fas expression in TEC incubated with healthy plasma or septic plasma before and after (Septic + CG161 M) Amberchrom resin adsorption. In c, nuclei were counterstained by 1 μg/ml propidium iodide (×200 magnification). In d, Kolomogorov Smirnov statistical analysis was performed.