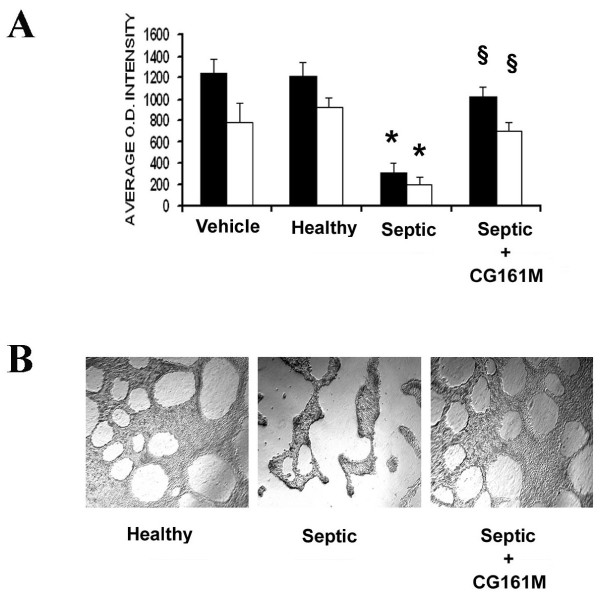
Figure 7.
Effect of resin adsorption on septic plasma-induced alteration of adhesion to matrixes and TEC morphogenesis. (a) In vitro adhesion assay of tubular epithelial cells (TEC) to extracellular matrixes. Septic plasma induced a significant decrease of adhesion of TEC to Type IV collagen/fibronectin (dark columns) or Matrigel (white columns) (*P < 0.05 Septic vs. Healthy or Vehicle). In contrast, Amberchrom resin adsorption significantly decreased the inhibitory effect of septic plasma on TEC adhesion to all matrixes tested (§P < 0.05 Septic + CG161 M vs. Septic). Data are expressed as average O.D. intensity ± standard deviation. Analysis of variance with Newmann-Keuls multicomparison test was performed. (b) Representative micrographs of TEC morphogenesis after 48 hours culture on Matrigel-coated plates in presence of control healthy plasma or septic plasma before and after (septic + CG161 M) Amberchrom resin adsorption.