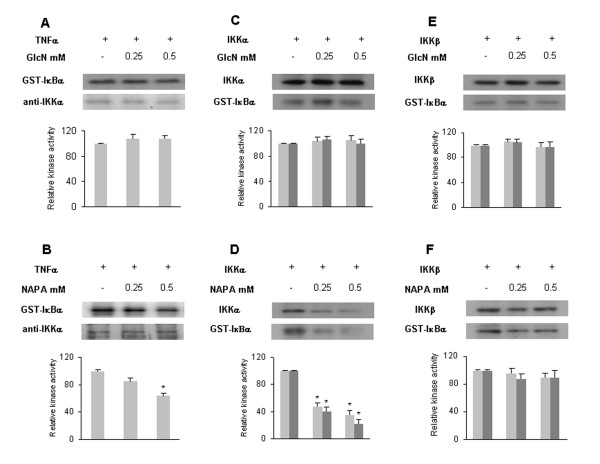
Figure 3.
Effect of glucosamine (GlcN) and NAPA on inhibitor κB kinase (IKK) kinase activity. HTB-94 cells were stimulated for 10 minutes with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα), IKK complex was immunoprecipitated from whole-cell extract with an anti-IKKα antibody and an in vitro kinase assay was performed. (a) Kinase assay on recombinant glutatione S-transferase (GST)-IκBα in the absence (-) or presence of 0.25 and 0.5 mM GlcN. (b) Kinase assay on recombinant GST-IκBα in the absence (-) or presence of 0.25 and 0.5 mM NAPA. Normalization was obtained by Western blot analysis using anti-IKKα antibody. (c) IKKα kinase activity on itself, using IKKα recombinant protein, in the absence (-) or presence of 0.25 and 0.5 mM GlcN. (d) IKKα kinase activity on GST-IκB substrate in the absence (-) or presence of 0.25 and 0.5 mM NAPA. (e) IKKβ kinase activity on itself, using IKKβ recombinant protein, in the absence (-) or presence of 0.25 and 0.5 mM GlcN. (f) IKKβ kinase activity on GST-IκB substrate in the absence (-) or presence of 0.25 and 0.5 mM NAPA. Grey bars indicate auto-phosphorylation of IKKα or IKKβ as indicated, and dark grey bars show GST-IκBα phosphorylation. *P ≤ 0.05. Results are expressed as fold change with respect to control. NAPA, 2-(N-Acetyl)-L-phenylalanylamido-2-deoxy-β-D-glucose.